Establishment and Application of Duplex Recombinase-Aided Amplification Combined with Lateral Flow Dipsticks for Rapid and Simultaneous Visual Detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus in Milk
- PMID: 40002017
- PMCID: PMC11854758
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14040573
Establishment and Application of Duplex Recombinase-Aided Amplification Combined with Lateral Flow Dipsticks for Rapid and Simultaneous Visual Detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus in Milk
Abstract
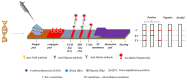
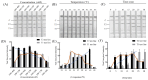
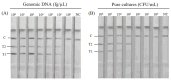
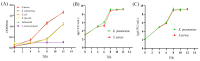
Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumoniae are significant and prevalent pathogens associated with bovine mastitis on dairy farms worldwide, resulting in severe infections in both dairy cows and, subsequently, human beings. Fast and dependable pathogen diagnostics are essential to minimize the effects of cow mastitis and human infections. The aim of this research was to develop a duplex recombinase-aided amplification (RAA) combined with the lateral flow dipstick (LFD) method, which was used for rapid, simultaneous detection of S. aureus and K. pneumoniae. The SKII culture medium for S. aureus and K. pneumoniae cocultivation was developed in this study. By optimizing the duplex RAA-LFD reaction conditions in terms of primer concentration, amplification temperature, and reaction time, the duplex RAA-LFD assay could successfully detect S. aureus and K. pneumoniae when the reaction was conducted at 39 °C for 20 min. The duplex RAA-LFD method demonstrated good specificity, exhibiting no cross-reactivity with other pathogens. In addition, the detection limit of the duplex RAA-LFD for S. aureus and K. pneumoniae was 60 fg of genomic DNA and 1.78 × 103 and 2.46 × 103 CFU/mL of bacteria in pure culture. Moreover, the duplex RAA-LFD technique is capable of identifying S. aureus and K. pneumoniae in artificially spiked milk samples even at very low initial concentrations of 1.78 × 101 and 2.46 × 100 CFU/mL, respectively, after 6 h of enrichment. The result of the actual samples showed that the total concordance rate of the duplex RAA-LFD method with the biochemical identification method and PCR method could reach 92.98~98.25% with high consistency. The results of this study indicated that the duplex RAA-LFD assay, which is a precise, sensitive, and simple field testing technique, can be used to identify S. aureus and K. pneumoniae and is expected to be used for disease diagnosis.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae; Staphylococcus aureus; lateral flow dipstick; rapid detection; recombinase-aided amplification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships related to this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development of an isothermal recombinase-aided amplification assay for the rapid and visualized detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae.J Sci Food Agric. 2022 Jul;102(9):3879-3886. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.11737. Epub 2022 Jan 7. J Sci Food Agric. 2022. PMID: 34936095
-
Rapid visual detection of Helicobacter pylori and vacA subtypes by Dual-Target RAA-LFD assay.Clin Chim Acta. 2025 Jan 1;564:119927. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2024.119927. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Clin Chim Acta. 2025. PMID: 39153656
-
Duplex recombinase aided amplification-lateral flow dipstick assay for rapid distinction of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium complex.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Oct 10;14:1454096. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1454096. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39450337 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid detection of cagA-positive Helicobacter pylori based on duplex recombinase aided amplification combined with lateral flow dipstick assay.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2022 May;103(1):115661. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2022.115661. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35305327
-
Establishment of reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification-lateral-flow dipstick and real-time fluorescence-based reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification methods for detection of the Newcastle disease virus in chickens.Poult Sci. 2020 Jul;99(7):3393-3401. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.03.018. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 32616233 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Titouche Y., Akkou M., Djaoui Y., Mechoub D., Fatihi A., Campaña-Burguet A., Bouchez P., Bouhier L., Houali K., Torres C., et al. Nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus in healthy dairy cows in Algeria: Antibiotic resistance, enterotoxin genes and biofilm formation. BMC Vet. Res. 2024;20:247. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04103-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abdullahi I.N., Lozano C., Ruiz-Ripa L., Fernández-Fernández R., Zarazaga M., Torres C. Ecology and Genetic Lineages of Nasal Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA Carriage in Healthy Persons with or without Animal-Related Occupational Risks of Colonization: A Review of Global Reports. PLoS Pathog. 2021;10:1000. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10081000. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Geng Y.Y., Liu S.Y., Wang J.F., Nan H.Z., Liu L.B., Sun X.X., Li D.Y., Liu M., Wang J.C., Tan K. Rapid Detection of Staphylococcus aureus in food using a Recombinase Polymerase Amplification-based assay. Food Anal. Methods. 2018;11:2847–2856. doi: 10.1007/s12161-018-1267-1. - DOI
-
- Filipello V., Bonometti E., Campagnani M., Bertoletti I., Romano A., Zuccon F., Campanella C., Losio M.N., Finazzi G. Investigation and Follow-Up of a Staphylococcal Food Poisoning Outbreak Linked to the Consumption of Traditional Hand-Crafted Alm Cheese. PLoS Pathog. 2020;9:1064. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9121064. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

