Effect of Food Matrix on Regulation of Intestinal Barrier and Microbiota Homeostasis by Polysaccharides Sulfated Carrageenan
- PMID: 40002079
- PMCID: PMC11854102
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14040635
Effect of Food Matrix on Regulation of Intestinal Barrier and Microbiota Homeostasis by Polysaccharides Sulfated Carrageenan
Abstract
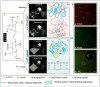
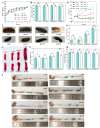
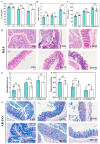
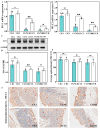
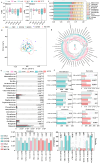
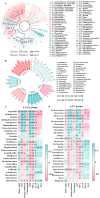
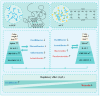
Carrageenan (CGN) has side effects on the intestinal barrier. Damage to the intestinal barrier is associated with exposure to sulfate groups. Food matrix has significant influence on the exposure quantity of sulfate groups and conformation in κ-CGN, but the corresponding side effects are not reported specifically. This study aimed to explore the regulatory effect of κ-CGN dissolved in aqueous (κ-CGN) and in 3% casein (κ-carrageenan-casein, κ-CC) on the intestinal barrier and microbiota homeostasis. Research has shown that both κ-CGN and κ-CC can induce different extents of intestinal barrier damage through disrupting microbiota homeostasis. Importantly, κ-CGN in casein with lower sulfate groups content was found to repair the intestinal barrier injury induced by an equivalent dose of κ-CGN aqueous through increasing the abundance of Oscillibacter and decreasing Weissella. These alleviating effects were reflected in lower levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and C-reaction protein (CRP), higher levels of interleukin (IL)-10, raised secretion of mucus and goblet cells, and improved expression of epithelial cell compact proteins zonula occluden (ZO)-1 and mucin protein 2 (MUC2). This study states that κ-CGN in casein has a positive regulatory effect on the intestinal barrier damage compared to in aqueous solution, which can provide guidance for processing and utilization of CGN.
Keywords: Oscillibacter; carrageenan; casein; gut microbiota; intestinal barrier; sulfate group.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are approved by all authors for publication and declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of physiological pH on the molecular characteristics, rheological behavior, and molecular dynamics of κ-carrageenan/casein.Front Nutr. 2023 Apr 14;10:1174888. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1174888. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37125034 Free PMC article.
-
κ-carrageenan induces the disruption of intestinal epithelial Caco-2 monolayers by promoting the interaction between intestinal epithelial cells and immune cells.Mol Med Rep. 2013 Dec;8(6):1635-42. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2013.1726. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Mol Med Rep. 2013. PMID: 24126493
-
Molecular signature of kappa-carrageenan mimics chondroitin-4-sulfate and dermatan sulfate and enables interaction with arylsulfatase B.J Nutr Biochem. 2012 Sep;23(9):1058-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.05.012. Epub 2011 Nov 12. J Nutr Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22079206
-
Food additive carrageenan: Part II: A critical review of carrageenan in vivo safety studies.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2014 Mar;44(3):244-69. doi: 10.3109/10408444.2013.861798. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24467586 Review.
-
The Role of Carrageenan in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Allergic Reactions: Where Do We Stand?Nutrients. 2021 Sep 27;13(10):3402. doi: 10.3390/nu13103402. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34684400 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Carrageenan: structure, properties and applications with special emphasis on food science.RSC Adv. 2025 Jun 27;15(27):22035-22062. doi: 10.1039/d5ra03296b. eCollection 2025 Jun 23. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40584756 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Campo V.L., Kawano D.F., Silva D.B.D., Carvalho I. Carrageenans: Biological properties, chemical modifications and structural analysis–A review. Carbohydr Polym. 2009;77:167–180. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.01.020. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

