WBP5 Expression Influences Prognosis and Treatment Response in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 40002180
- PMCID: PMC11852431
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17040587
WBP5 Expression Influences Prognosis and Treatment Response in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Erratum in
-
Correction: Jeong et al. WBP5 Expression Influences Prognosis and Treatment Response in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 587.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 29;17(15):2493. doi: 10.3390/cancers17152493. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805299 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objectives: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is characterized by complex genetic alterations. This study aimed to identify WBP5 as a promising therapeutic target and evaluate the effect of WBP5 expression on prognosis and treatment response in HNSCC.
Methods: Publicly available datasets were comprehensively analyzed to investigate WBP5 expression through comprehensive bioinformatics analysis and functional validation.
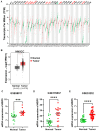
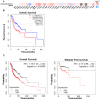
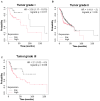
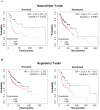
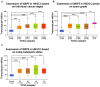
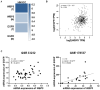
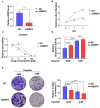
Results: WBP5 was particularly overexpressed in HNSCC, as analyzed through the Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis version 2 (GEPIA2) database and validated using multiple Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets. Analysis with UALCAN confirmed that WBP5 expression was significantly higher in advanced cancer stages and tumor grades than that of normal samples. A Kaplan-Meier analysis demonstrated that patients overexpressing WBP5 had a poor prognosis. Moreover, WBP5 expression correlated with the overexpression of the epidermal growth factor receptor in HNSCC. In vitro experiments revealed that WBP5 knockdown significantly reduced FaDu cell proliferation and viability. Furthermore, silencing WBP5 enhanced cisplatin sensitivity, indicating its potential role in chemoresistance.
Conclusions: These results indicate that WBP5 could act as a prognostic marker and a viable therapeutic target in HNSCC. Modulating WBP5 expression may represent a novel strategy to enhance treatment efficacy. Future studies should elucidate the precise mechanisms of WBP5 action and develop targeted therapies. This integrated approach, combining a comprehensive analysis of publicly available datasets with in vitro experimental validation provides strong evidence for the clinical significance of WBP5 in HNSCC.
Keywords: Transcriptional Elongation Factor A-like 9 (TCEAL9); WW domain-binding protein 5 (WBP5); head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CCDC71L as a novel prognostic marker and immunotherapy target via lipid metabolism in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024 Dec;125(6):101799. doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2024.101799. Epub 2024 Feb 16. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024. PMID: 38367702
-
Identification of a telomere-related gene signature for the prognostic and immune landscape prediction in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by integrated analysis of machine learning and Mendelian randomization.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Apr 18;104(16):e42211. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042211. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40258723 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of senescence-related gene FEN1 on neuroblastoma progression and cisplatin chemotherapy sensitivity.Oncol Res. 2025 Jun 26;33(7):1695-1708. doi: 10.32604/or.2025.060021. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40612863 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Correction: Jeong et al. WBP5 Expression Influences Prognosis and Treatment Response in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 587.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 29;17(15):2493. doi: 10.3390/cancers17152493. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805299 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gylfe A.E., Kondelin J., Turunen M., Ristolainen H., Katainen R., Pitkanen E., Kaasinen E., Rantanen V., Tanskanen T., Varjosalo M., et al. Identification of candidate oncogenes in human colorectal cancers with microsatellite instability. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:540–543.e522. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.05.015. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

