Comparison of Survival Outcomes of Breast-Conserving Surgery Plus Radiotherapy with Mastectomy in Early Breast Cancer Patients: Less Is More?
- PMID: 40002186
- PMCID: PMC11852543
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17040591
Comparison of Survival Outcomes of Breast-Conserving Surgery Plus Radiotherapy with Mastectomy in Early Breast Cancer Patients: Less Is More?
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the survival outcomes of early-stage breast cancer patients treated with breast-conserving therapy (BCT) and mastectomy.
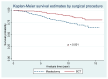
Method: This retrospective study includes 1330 early-stage breast cancer patients treated at Chiang Mai University (CMU) hospital, using data from the Chiang Mai Cancer Registry between 2004 and 2015. Information pertinent to patients and their treatment was collected for analysis. Time-to-event analysis was performed using Kaplan-Meier methods.
Results: The baseline characteristics of 1330 patients showed significant differences between the BCT and mastectomy groups in terms of age, tumor size, and tumor location. BCT patients were younger, had smaller tumors, and exhibited less nodal involvement. Propensity score matching created a balanced cohort of 534 patients where differences persisted in age and tumor size. Univariate analysis revealed significant survival associations for BCT, younger age, and smaller tumor size. Multivariate analysis confirmed these factors, with BCT showing an adjusted hazard ratio (HR) of 0.58 (95% CI: 0.36-0.93; p = 0.023) compared to mastectomy. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis demonstrated a significant survival advantage for BCT, particularly in HER2-enriched and triple-negative subtypes. The 15-year overall survival was 80.01% in the BCT group versus 64.33% in the mastectomy group (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: This study reveals key differences between outcomes following breast-conserving therapy (BCT) and mastectomy patients, including age and tumor characteristics. BCT showed improved overall survival, particularly in HER2-enriched and triple-negative breast cancers. However, our study's limitations may affect the results. These findings suggest that BCT may offer survival benefits for specific subtypes, highlighting the importance of personalized treatment approaches.
Keywords: breast-conserving therapy; early breast cancer; mastectomy; survival; survival outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this study. All authors have disclosed any financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence (bias) their work. This research was conducted with financial support from the Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University. The funders had no role in this study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University. The authors are responsible for the content and writing of this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of Breast-Conserving Surgery and Mastectomy on the Survival of Patients with Early-Stage (T1-2N0-1M0) HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis.Oncol Res Treat. 2023;46(12):511-519. doi: 10.1159/000534856. Epub 2023 Nov 6. Oncol Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 37931609
-
Long-term overall survival of patients who undergo breast-conserving therapy or mastectomy for early operable HER2-Positive breast cancer after preoperative systemic therapy: an observational cohort study.Lancet Reg Health Am. 2024 Mar 8;32:100712. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2024.100712. eCollection 2024 Apr. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2024. PMID: 38495316 Free PMC article.
-
Breast-conserving therapy is associated with better survival than mastectomy in Early-stage breast cancer: A propensity score analysis.Cancer Med. 2022 Apr;11(7):1646-1658. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4510. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 35212160 Free PMC article.
-
Breast-conserving therapy leads to better survival outcomes compared to mastectomy in patients with early breast cancer: evidences from the recent literature.Minerva Surg. 2023 Apr;78(2):183-193. doi: 10.23736/S2724-5691.22.09820-3. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Minerva Surg. 2023. PMID: 36651505 Review.
-
Should patients with early breast cancer still be offered the choice of breast conserving surgery or mastectomy?Eur J Surg Oncol. 2016 Nov;42(11):1636-1641. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2016.08.016. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27665053 Review.
Cited by
-
Breast-Conserving Oncoplastic Surgery Stratification: Morbidity Retrospective Analysis and its Association with Procedure Complexity Level.Ann Surg Oncol. 2025 Jul 20. doi: 10.1245/s10434-025-17838-0. Online ahead of print. Ann Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40685460
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

