The Role of MRI Radiomics Using T2-Weighted Images and the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Map for Discriminating Between Warthin's Tumors and Malignant Parotid Gland Tumors
- PMID: 40002215
- PMCID: PMC11852730
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17040620
The Role of MRI Radiomics Using T2-Weighted Images and the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Map for Discriminating Between Warthin's Tumors and Malignant Parotid Gland Tumors
Abstract
Background/objectives: Differentiating between benign and malignant parotid gland tumors (PGT) is essential for establishing the treatment strategy, which is greatly influenced by the tumor's histology. The objective of this study was to evaluate the role of MRI-based radiomics in the differentiation between Warthin's tumors (WT) and malignant tumors (MT), two entities that proved to present overlapping imaging features on conventional and functional MRI sequences.
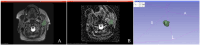
Methods: In this retrospective study, a total of 106 PGT (66 WT, 40 MT) with confirmed histology were eligible for radiomic analysis, which were randomly split into a training group (79 PGT; 49 WT; 30 MT) and a testing group (27 PGT; 17 WT, 10 MT). The radiomic features were extracted from 3D segmentations of PGT performed on the following sequences: PROPELLER T2-weighted images and the ADC map, using a dedicated software. First- and second-order features were derived for each lesion, using original and filtered images.
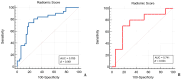
Results: After employing several feature reduction techniques, including LASSO regression, three final radiomic parameters were identified to be the most significant in distinguishing between the two studied groups, with fair AUC values that ranged between 0.703 and 0.767. All three radiomic features were used to construct a Radiomic Score that presented the highest diagnostic performance in distinguishing between WT and MT, achieving an AUC of 0.785 in the training set, and 0.741 in the testing set.
Conclusions: MRI-based radiomic features have the potential to serve as promising novel imaging biomarkers for discriminating between Warthin's tumors and malignant tumors in the parotid gland. Nevertheless, it is still to prove how radiomic features can consistently achieve higher diagnostic performance, and if they can outperform alternative imaging methods, ideally in larger, multicentric studies.
Keywords: MRI; Warthin’s tumors; malignant tumors; parotid gland tumors; radiomics; textural analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Role of an MRI-Based Radiomic Signature in Predicting Malignancy of Parotid Gland Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 23;15(13):3319. doi: 10.3390/cancers15133319. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444429 Free PMC article.
-
MRI-Based Radiomics to Differentiate between Benign and Malignant Parotid Tumors With External Validation.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 27;11:656918. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.656918. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33987092 Free PMC article.
-
Parotid gland tumors: comparison of conventional and diffusion-weighted MRI findings with histopathological results.Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2021 May 1;50(4):20200391. doi: 10.1259/dmfr.20200391. Epub 2020 Dec 11. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33237812 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Warthin's Tumors of the Parotid Gland With Radiofrequency Ablation: A Systematic Review of the Current Literature.Ear Nose Throat J. 2024 Apr 22:1455613241248119. doi: 10.1177/01455613241248119. Online ahead of print. Ear Nose Throat J. 2024. PMID: 38647239 Review.
-
Bilateral Warthin's tumour of the parotid gland: a 16-year retrospective analysis and systematic review.J Laryngol Otol. 2024 May;138(5):559-564. doi: 10.1017/S0022215123001834. Epub 2023 Nov 3. J Laryngol Otol. 2024. PMID: 37920099
References
-
- El-Naggar A.K., Chan J.K.C., Grandis J.R., Takata T., Slootweg P.J., editors. WHO Classification of Head and Neck Tumours. 4th ed. IARC; Lyon, France: 2017.
-
- Tartaglione T., Botto A., Sciandra M., Gaudino S., Danieli L., Parrilla C., Paludetti G., Colosimo C. Differential diagnosis of parotid gland tumours: Which magnetic resonance findings should be taken in account? Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2015;35:314–320. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-693. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

