Recent Anti-KRASG12D Therapies: A "Possible Impossibility" for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 40002297
- PMCID: PMC11853620
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17040704
Recent Anti-KRASG12D Therapies: A "Possible Impossibility" for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
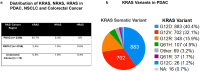
Background: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is an aggressive cancer, able to thrive in a challenging tumor microenvironment. Current standard therapies, including surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and chemoradiation, have shown a dismal survival prognosis, resulting in less than a year of life in the metastatic setting. Methods: The pressing need to find better therapeutic methods brought about the discovery of new targeted therapies against the infamous KRAS mutations, the major oncological drivers of PDAC. Results: The most common KRAS mutation is KRASG12D, which causes a conformational change in the protein that constitutively activates downstream signaling pathways driving cancer hallmarks. Novel anti-KRASG12D therapies have been developed for solid-organ tumors, including small compounds, pan-RAS inhibitors, protease inhibitors, chimeric T cell receptors, and therapeutic vaccines. Conclusions: This comprehensive review summarizes current knowledge on the biology of KRAS-driven PDAC, the latest therapeutic options that have been experimentally validated, and developments in ongoing clinical trials.
Keywords: KRASG12D; PDAC; targeted therapies; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

