Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Efficacy of Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum) Leaves: Implications for Sustainable Cosmeceutical Development
- PMID: 40002388
- PMCID: PMC11852302
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14020202
Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Efficacy of Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum) Leaves: Implications for Sustainable Cosmeceutical Development
Abstract
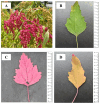
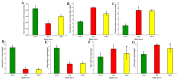
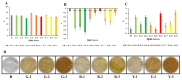
Chenopodium formosanum (djulis), well known for its vivid color variation during diverse senescence stages, has attracted attention for its perceived health benefits and antioxidant capacity. Djulis leaves, often discarded as biowaste after harvesting, were evaluated for their potential as a source of antioxidant compounds. The current study analyzes the physicochemical and antioxidant activities of red, green, and yellow djulis leaf extracts across various senescence stages to probe their prospective utility in cosmeceuticals. Various plant compounds including total carbohydrates, phenolics and flavonoids, chlorophyll a and b, and betaxanthins and betacyanins were measured using spectrophotometric techniques. Antioxidant potential was assessed using DPPH, FRAP, CUPRAC, TEAC, and DMPD assays. Green djulis leaves displayed elevated total carbohydrate and chlorophyll levels, whereas red djulis leaves exhibited heightened phenolic, flavonoid, betaxanthin, and betacyanin content, indicating its suitability for cosmeceutical applications. Antioxidant evaluations revealed substantial disparities among the extracts, with red djulis leaf extract demonstrating superior antioxidant activity in most assays. These findings revealed the distinct antioxidant profiles of djulis leaf extracts influenced by color and senescence stage. These findings advance our understanding of the bioactive attributes of djulis leaves and their potential for incorporation into functional products.
Keywords: Chenopodium formosanum; antioxidant; cosmeceuticals; djulis leaves.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Cheng Y.-T., Lu W.-C., Chan Y.-J., Huang P.-H., Chiang P.-Y., Chen R.-S., Li P.-H. Effect of extruded djulis (Chenopodium formosanum) snacks on the ameliorative potential against diabetic cardiomyopathy. J. Funct. Foods. 2024;116:106154. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2024.106154. - DOI
-
- Chio E.H., Yang E.-C., Huang H.-T., Hsu E.-L., Chen C.-R., Huang C.-G., Huang R.-N. Toxicity and repellence of Taiwanese indigenous djulis, Chenopodium formosaneum, against Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) and Forcipomyia taiwana (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) J. Pest Sci. 2013;86:705–712. doi: 10.1007/s10340-013-0500-3. - DOI
-
- Chu C.-C., Chen S.-Y., Chyau C.-C., Wang S.-C., Chu H.-L., Duh P.-D. Djulis (Chenopodium formosanum) and its bioactive compounds protect human lung epithelial A549 cells from oxidative injury induced by particulate matter via Nrf2 signaling pathway. Molecules. 2021;27:253. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010253. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

