Crosstalk Between Antioxidants and Adipogenesis: Mechanistic Pathways and Their Roles in Metabolic Health
- PMID: 40002389
- PMCID: PMC11852089
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14020203
Crosstalk Between Antioxidants and Adipogenesis: Mechanistic Pathways and Their Roles in Metabolic Health
Abstract
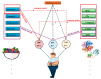
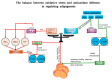
The interplay between oxidative stress and adipogenesis is a critical factor in the development of obesity and its associated metabolic disorders. Excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) disrupt key transcription factors such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPα), impairing lipid metabolism, promoting adipocyte dysfunction, and exacerbating inflammation and insulin resistance. Antioxidants, classified as endogenous (e.g., glutathione, superoxide dismutase, and catalase) and exogenous (e.g., polyphenols, flavonoids, and vitamins C and E), are pivotal in mitigating these effects by restoring redox balance and preserving adipocyte functionality. Endogenous antioxidants neutralize ROS and safeguard cellular structures; however, under heightened oxidative stress, these defenses are often insufficient, necessitating dietary supplementation. Exogenous antioxidants derived from plant-based sources, such as polyphenols and vitamins, act through direct ROS scavenging, upregulation of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, and modulation of key signaling pathways like nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and PPARγ, reducing lipid peroxidation, inflammation, and adipocyte dysfunction. Furthermore, they influence epigenetic regulation and transcriptional networks to restore adipocyte differentiation and limit lipid accumulation. Antioxidant-rich diets, including the Mediterranean diet, are strongly associated with improved metabolic health, reduced obesity rates, and enhanced insulin sensitivity. Advances in personalized antioxidant therapies, guided by biomarkers of oxidative stress and supported by novel delivery systems, present promising avenues for optimizing therapeutic interventions. This review, "Crosstalk Between Antioxidants and Adipogenesis: Mechanistic Pathways and Their Role in Metabolic Health", highlights the mechanistic pathways by which antioxidants regulate oxidative stress and adipogenesis to enhance metabolic health.
Keywords: C/EBPα; PPARγ; adipogenesis; endogenous antioxidants; epigenetic mechanisms; insulin resistance; natural antioxidants; obesity; oxidative stress; personalized antioxidant therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel insights of dietary polyphenols and obesity.J Nutr Biochem. 2014 Jan;25(1):1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.09.001. J Nutr Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24314860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pycnogenol® inhibits lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes with the modulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production associated with antioxidant enzyme responses.Phytother Res. 2012 Mar;26(3):403-11. doi: 10.1002/ptr.3568. Epub 2011 Jul 27. Phytother Res. 2012. PMID: 21796705
-
Differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into fat involves reactive oxygen species and Forkhead box O1 mediated upregulation of antioxidant enzymes.Stem Cells Dev. 2013 Mar 15;22(6):878-88. doi: 10.1089/scd.2012.0306. Epub 2012 Nov 12. Stem Cells Dev. 2013. PMID: 23025577 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: chronic diseases and aging.Arch Toxicol. 2023 Oct;97(10):2499-2574. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03562-9. Epub 2023 Aug 19. Arch Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37597078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-oxidative and anti-adipogenic effects of caffeine in an in vitro model of Graves' orbitopathy.Endocr J. 2020 Apr 28;67(4):439-447. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ19-0521. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Endocr J. 2020. PMID: 31941844
Cited by
-
Potential Roles of Natural Antioxidants in Modulating Neurodegenerative Disease Pathways.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;62(8):10367-10397. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04874-w. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40202704 Review.
-
Antioxidants and Reactive Oxygen Species: Shaping Human Health and Disease Outcomes.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 4;26(15):7520. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157520. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant Defense and Redox Signaling in Elite Soccer Players: Insights into Muscle Function, Recovery, and Training Adaptations.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jul 2;14(7):815. doi: 10.3390/antiox14070815. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722919 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Phelps N.H., Singleton R.K., Zhou B., Heap R.A., Mishra A., Bennett J.E., Paciorek C.J., Lhoste V.P.F., Carrillo-Larco R.M., Stevens G.A., et al. Worldwide trends in underweight and obesity from 1990 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 3663 population-representative studies with 222 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet. 2024;403:1027–1050. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)02750-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sysoeva V.Y., Lazarev M.A., Kulebyakin K.Y., Semina E.V., Rubina K.A. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Governing Adipogenic Differentiation. Russ. J. Dev. Biol. 2023;54:S10–S22. doi: 10.1134/S1062360423070068. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

