Optimization of Supercritical Fluid Extraction for the Recovery of γ-Oryzanol-Rich Extracts with Improved Bioactivity from Rice Bran
- PMID: 40002392
- PMCID: PMC11852124
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14020206
Optimization of Supercritical Fluid Extraction for the Recovery of γ-Oryzanol-Rich Extracts with Improved Bioactivity from Rice Bran
Abstract
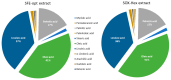
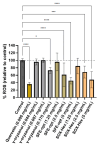
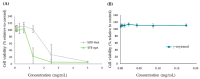
Rice bran (RB) is a rice processing by-product recognized to be a source of bioactive compounds, including γ-oryzanol and fatty acids, which have interesting bioactivities such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. This study aims to optimize the supercritical fluid extraction process for recovering these high-value compounds from rice bran with improved bioactivity. A Central Composite Face-Centered Design was employed to optimize the extraction process by varying the temperature (40-80 °C) and pressure (200-500 bar). The optimal extraction conditions were identified at 500 bar and 62 °C that led to the extraction of 17.3% mass yield with 784.5 mg of fatty acids and 36.6 mg of γ-oryzanol per gram of extract, striking a balance between extraction yield and bioactive concentrations. When compared with conventional extractions with n-hexane, supercritical fluid extraction showed similar global yield (18.0 vs. 17.3%) and FA concentration (130.14 vs. 135.70 mg/g of RB) but higher selectivity and extraction yield for γ-oryzanol (18.0 vs. 36.4 mg/g extract; 3.3 vs. 6.3 mg/g of RB). Cellular antioxidant activity assays showed that both extracts reduced the quantity of reactive oxygen species (ROS) up to 50% in Caco-2 cells submitted to oxidative stress. Importantly, supercritical fluid extract was more effective in inhibiting colorectal cancer cell growth (EC50 = 0.9 mg/mL vs. 1.15 mg/mL) than the hexane extract, and this effect was more pronounced than that obtained for pure γ-oryzanol in the same concentration range. These findings highlight the potential of supercritical fluid technology to develop rice bran extracts with antioxidant and antiproliferative properties, underlining the promising applications of this technology in the field of natural product extraction.
Keywords: antioxidant activity; antiproliferative effect; green extraction; rice bran oil; supercritical CO2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bioactives from Crude Rice Bran Oils Extracted Using Green Technology.Molecules. 2023 Mar 7;28(6):2457. doi: 10.3390/molecules28062457. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36985429 Free PMC article.
-
Recovery of γ-Oryzanol from Rice Bran Acid Oil by an Acid-base Extraction Method with the Assistance of Response Surface Methodology.J Oleo Sci. 2018;67(11):1405-1415. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess18073. J Oleo Sci. 2018. PMID: 30404961
-
Concentrations of tocols and γ-oryzanol compounds in rice bran oil obtained by fractional extraction with supercritical carbon dioxide.J Oleo Sci. 2014;63(1):47-53. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess13144. Epub 2013 Dec 24. J Oleo Sci. 2014. PMID: 24371195
-
Rice bran nutraceutics: A comprehensive review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017 Nov 22;57(17):3771-3780. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2016.1164120. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017. PMID: 27015585 Review.
-
Composition, Microbiota, Mechanisms, and Anti-Obesity Properties of Rice Bran.Foods. 2023 Mar 18;12(6):1300. doi: 10.3390/foods12061300. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36981226 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plant-Derived Nanovesicles from Soaked Rice Water: A Novel and Sustainable Platform for the Delivery of Natural Anti-Oxidant γ-Oryzanol.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jun 12;14(6):717. doi: 10.3390/antiox14060717. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563350 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Punia S., Kumar M., Sandhu K.S., Whiteside W.S. Rice-bran oil: An emerging source of functional oil. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021;45:e15318. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.15318. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

