Exploring Cardiac Sympathetic Denervation in Transthyretin-Mediated Hereditary Amyloidosis (ATTRv): Insights from 123I-mIBG Scintigraphy
- PMID: 40002660
- PMCID: PMC11854682
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15040508
Exploring Cardiac Sympathetic Denervation in Transthyretin-Mediated Hereditary Amyloidosis (ATTRv): Insights from 123I-mIBG Scintigraphy
Abstract
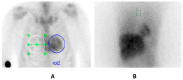
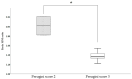
Background/Objectives: Hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis (ATTRv) is a rare disease characterized by the deposition of amyloid in the heart and peripheral nerves, particularly affecting small fibers. This study aims to evaluate autonomic cardiac involvement in ATTRv. Methods: Twelve patients with ATTRv and twelve sex- and age-matched healthy subjects underwent 123I-mIBG scintigraphy to evaluate the early and late heart-to-mediastinum ratio (eH/M and lH/M), 99mTc-HDP bone scan scintigraphy, and neurophysiological assessments. Data were analyzed in relation to functional cardiac and neurologic scales (NYHA and FAP scales). Results: Patients with ATTRv exhibited significant cardiac denervation, as demonstrated by the reduction in early and late H/M ratios compared to the control group (eH/M: 1.48 ± 0.08 vs. 1.89 ± 0.05, p < 0.001; lH/M: 1.39 ± 0.08 vs. 2.01 ± 0.05, p < 0.001). Values of eH/M and lH/M < 1.6 effectively differentiated patients with ATTRv from the healthy controls. Cardiac denervation correlated with interventricular septal thickness and the Perugini score but was not related to neurophysiological assessments or NYHA and FAP scales. Conclusions: Ultimately, 123I-mIBG scintigraphy is an effective tool for assessing cardiac denervation in patients with ATTRv.
Keywords: 123I-mIBG scintigraphy; ATTRv; amyloidosis; heart denervation; transthyretin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

