Sarcopenia in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Narrative Review from Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Approaches
- PMID: 40002765
- PMCID: PMC11852367
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13020352
Sarcopenia in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Narrative Review from Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Approaches
Abstract
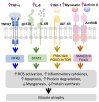
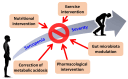
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a progressive condition linked to sarcopenia, a syndrome characterized by loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength, affecting a quarter of CKD patients globally. Sarcopenia has multiple paths through which it can worsen morbidity and mortality as well as decrease the quality of life in CKD, including systemic inflammation, hormonal imbalances, metabolic changes, and dysbiosis of gut microbiota. There is a regional variation in the criteria set for diagnosis, with two main groups being the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People and the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. Management regimes such as nutritional optimization, vitamin D, exercise, correction of metabolic acidosis, and modulation of gut microbiota constitute effective intervention strategies. Emerging therapeutic options include anabolic agents, myostatin inhibitors, and anti-inflammatory treatment options. Future advances such as genomics, proteomics, and personalized medicine will open up new avenues for addressing the complex pathophysiology of sarcopenia. Hence, a comprehensive multidisciplinary approach focused on the specific needs of each patient will be vital in reducing the effects of sarcopenia and improving the situation of people with CKD.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; diagnostic criteria; muscle synthesis; muscle wasting; pathophysiology; sarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Moisi M.I., Bungau S.G., Vesa C.M., Diaconu C.C., Behl T., Stoicescu M., Toma M.M., Bustea C., Sava C., Popescu M.I. Framing Cause-Effect Relationship of Acute Coronary Syndrome in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Diagnostics. 2021;11:1518. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11081518. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

