Therapeutic Targets and Approaches to Manage Inflammation of NAFLD
- PMID: 40002806
- PMCID: PMC11853636
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13020393
Therapeutic Targets and Approaches to Manage Inflammation of NAFLD
Abstract
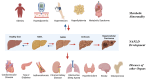
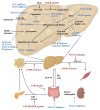
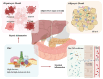
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its advanced form, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), are the leading causes of chronic liver disease globally. They are driven by complex mechanisms where inflammation plays a pivotal role in disease progression. Current therapies, including lifestyle changes and pharmacological agents, are limited in efficacy, particularly in addressing the advanced stages of the disease. Emerging approaches targeting inflammation, metabolic dysfunction, and fibrosis offer promising new directions, though challenges such as treatment complexity and heterogeneity persist. This review concludes the main therapeutic targets and approaches to manage inflammation currently and emphasizes the critical need for future drug development and combination therapy for NAFLD/NASH management.
Keywords: NAFLD; NASH; inflammation; pathophysiology; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kleiner D.E., Brunt E.M., Van Natta M., Behling C., Contos M.J., Cummings O.W., Ferrell L.D., Liu Y.C., Torbenson M.S., Unalp-Arida A., et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;41:1313–1321. doi: 10.1002/hep.20701. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 82073184/The National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022-4-4019/The capital health research and development of special
- 2022-PUMCH-A-071/The National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding
- 2022-PUMCH-B-024/National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding
- 82470700/The National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

