The mTOR Signaling Pathway: Key Regulator and Therapeutic Target for Heart Disease
- PMID: 40002810
- PMCID: PMC11853667
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13020397
The mTOR Signaling Pathway: Key Regulator and Therapeutic Target for Heart Disease
Abstract
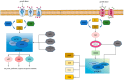
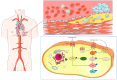
Heart disease, including myocardial infarction, heart failure, cardiac hypertrophy, and cardiomyopathy, remains a leading cause of mortality worldwide. The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a centrally regulated kinase that governs key cellular processes, including growth, proliferation, metabolism, and survival. Notably, mTOR plays a pivotal role in cardiovascular health and disease, particularly in the onset and progression of cardiac conditions. In this review, we discuss mTOR's structure and function as well as the regulatory mechanisms of its associated signaling pathways. We focus on the molecular mechanisms by which mTOR signaling regulates cardiac diseases and the potential of mTOR inhibitors and related regulatory drugs in preventing these conditions. We conclude that the mTOR signaling pathway is a promising therapeutic target for heart disease.
Keywords: heart disease; mTOR; signaling pathway; target.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting the mTOR-Autophagy Axis: Unveiling Therapeutic Potentials in Osteoporosis.Biomolecules. 2024 Nov 15;14(11):1452. doi: 10.3390/biom14111452. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39595628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in cardiac physiology and disease.Circ Res. 2014 Jan 31;114(3):549-64. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.302022. Circ Res. 2014. PMID: 24481845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting mTOR Kinase with Natural Compounds: Potent ATP-Competitive Inhibition Through Enhanced Binding Mechanisms.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Dec 12;17(12):1677. doi: 10.3390/ph17121677. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39770519 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal myocyte hypertrophy requires mTOR kinase activity and S6K1.Exp Cell Res. 2005 Sep 10;309(1):211-9. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.05.017. Exp Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 15963500
-
The mTOR Signaling Pathway in Myocardial Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Curr Diab Rep. 2017 Jun;17(6):38. doi: 10.1007/s11892-017-0865-4. Curr Diab Rep. 2017. PMID: 28434143 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of the Mechanisms of Astragaloside IV and Berberine in Vascular Dysfunction Associated with Obesity and Diabetes.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jun 7;19:4911-4932. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S520323. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40502549 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roth G.A., Mensah G.A., Johnson C.O., Addolorato G., Ammirati E., Baddour L.M., Barengo N.C., Beaton A.Z., Benjamin E.J., Benziger C.P., et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020;76:2982–3021. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adekoya A., Tyagi S.K., Duru C.N., Satia I., Paudyal V., Kurmi O.P. Effects of Household Air Pollution (HAP) on Cardiovascular Diseases in Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022;19:9298. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19159298. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

