Chronic Stress and Headaches: The Role of the HPA Axis and Autonomic Nervous System
- PMID: 40002876
- PMCID: PMC11852498
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13020463
Chronic Stress and Headaches: The Role of the HPA Axis and Autonomic Nervous System
Abstract
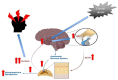
Chronic stress significantly influences the pathogenesis of headache disorders, affecting millions worldwide. This review explores the intricate relationship between stress and headaches, focusing on the dysregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and autonomic nervous system (ANS). Persistent stress could lead to neuroinflammation, increased pain sensitivity, and vascular changes that could contribute to headache development and progression. The bidirectional nature of this relationship creates a vicious cycle, with recurrent headaches becoming a source of additional stress. Dysregulation of the HPA axis and ANS imbalance could amplify susceptibility to headaches, intensifying their frequency and severity. While pharmacological interventions remain common, non-pharmacological approaches targeting stress reduction, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, biofeedback, and relaxation techniques, offer promising avenues for comprehensive headache management. By addressing the underlying stress-related mechanisms, these approaches provide a sustainable strategy to reduce headache frequency and improve patients' quality of life.
Keywords: HPA axis; autonomic nervous system; chronic stress; cortisol; migraines; neuroendocrine regulation; non-pharmacological treatments; stress-induced headaches; tension-type headaches.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources