Paediatric Major Trauma Psychology Service Evaluation: An Early Review of an Integrated Model of Care
- PMID: 40003343
- PMCID: PMC11854553
- DOI: 10.3390/children12020241
Paediatric Major Trauma Psychology Service Evaluation: An Early Review of an Integrated Model of Care
Abstract
Background: Major trauma is a leading cause of death and disability in children and young people (CYP) in the United Kingdom (UK). Since 2012, major trauma centres (MTCs) have been created with specialist expertise to treat patients suffering with lifechanging injuries. Much research has focused on the physical recovery of patients; however, the psychological and psychosocial impacts of major trauma are significant and often neglected/deprioritised. Less is known about this area in relation to a paediatric population.
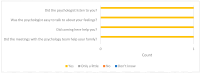
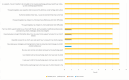
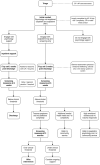
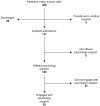
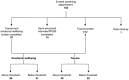
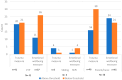
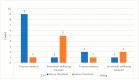
Methods: This service evaluation reports on the first year of an integrated psychological pathway within a London paediatric MTC. The proactive approach involves inpatient and outpatient psychological support, screening children and families for trauma symptoms and emotional distress, offering psychological intervention where required, and liaison with community mental health teams, social care services and third sector organisations. Descriptive statistics are reported on the patient demographics and mechanism of injury, as well as screening scores at 6 weeks and 3 months following the traumatic incident. Patient feedback is also presented.
Results: The results demonstrate a significant increase in the numbers of children and families offered psychological support following the creation of the pathway and an overwhelmingly positive response from service users.
Conclusions: Clinical implications are outlined, and areas for further development are discussed.
Keywords: PTSD; major trauma; paediatric mental health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Peden M., Oyegbite K., Ozanne-Smith J., Hyder A.A., Branche C., Rahman A., Rivara F., Bartolomeos K. World Report on Child Injury Prevention. World Health Organisation; Geneva, Switzerland: 2008. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

