Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole-Time-of-Flight-Mass Spectrometry-Based Analysis of Facial Physiological Parameters and Lipid Composition of Between Sensitive Skin of Women Aged 36-42 and 43-49 Year
- PMID: 40003584
- PMCID: PMC11856038
- DOI: 10.3390/life15020175
Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole-Time-of-Flight-Mass Spectrometry-Based Analysis of Facial Physiological Parameters and Lipid Composition of Between Sensitive Skin of Women Aged 36-42 and 43-49 Year
Abstract
Background: UPLC-Q-TOF-MS (Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry) is a high-precision, high-density technology for lipid analysis. Sensitive skin is a sub-stable condition, and it has been reported that the population of sensitive skin in China is predominantly female. Meanwhile, women with sensitive skin have different physiological parameters as well as lipid compositions at different ages. The Yellow Emperor's Classic of Internal Medicine states that the number of women's life cycles is seven, that major changes are manifested every 7 years, and that aging begins at age 35. At present, the correlation between facial lipid composition and aging indicators of sensitive skin in women aged 36-42 and 43-49 years has not been reported.
Objective: This study reveals the relationship between key lipid composition of the facial skin and the aging of sensitive skin in women aged 36-42 and 43-49 years.
Methods: We used UPLC-Q-TOF-MS technology to study the changes in lipid composition in the sensitive skin of woman aged 36-42 and 43-49 years, using a multi-probe adapter system with different types of skin-testing probes to test physiological parameters. Three types of multivariate data-questionnaires, physiological indicators, and lipid composition-were used together to assess differences in aging in a population of women with sensitive skin at different ages.
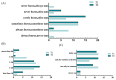
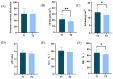
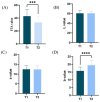
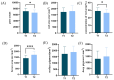
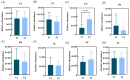
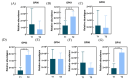
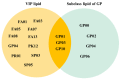
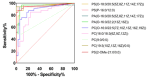
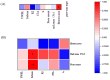
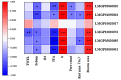
Results: 1. In the questionnaire part, the T1 group was more susceptible to sunburn and the T2 group was more susceptible to tanning. 2. In the physiological index part, the aging characteristics of facial skin in the T2 group were obvious, with the b-value, as well as the brown area size, being significantly higher than the T1 group, while the TWEL, sebum, R2 value, ITA value, pore count, and concentration of the red area were significantly lower than the T1 group. 3. In the lipid part, the total facial lipid content was higher in the T2 group, with a significantly higher GP lipid, and the 47 VIP lipids obtained were analyzed by ROC curves, narrowing down to six lipids, PS(2-OMe-21:0/0:0), PS(O-18:0/20:5 (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)), PA(O-16:0/20:5 (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)), PS (P-16:0/12:0, PA (O-16:0/22:2 (13Z,16Z)), and PC (19:3 (10Z,13Z,16Z)/0:0)), and all six lipids were higher in the T2 group. 4. In Spearman correlation analysis, PS(O-18:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)), PS(P-16:0/12:0), PS(2-OMe-21:0/0:0), PA(O-16:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)), and PC(19:3( 10Z,13Z,16Z)/0:0), which are five lipids and skin aging indicators (TWEL, sebum, ITA value, b-value, pore count, concentration of red area, and brown area size) were significantly correlated.
Conclusions: Through correlation analysis, it was found that changes in the composition of skin surface lipids (SSLs) in both age groups have an important influence on facial physiological indicators (aging manifestations) and played an important role in furthering the understanding of sensitive skin aging. Therefore, these lipid components also provide theoretical support for the development of cosmetic ingredients that slow down the aging of sensitive skin.
Keywords: age; correlation analysis; lipid; sensitive skin; skin aging.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum metabolic alterations in chickens upon infectious bursal disease virus infection.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Dec 19;20(1):569. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04402-3. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39696379 Free PMC article.
-
The eosinophil chemoattractant 5-oxo-ETE and the OXE receptor.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):651-65. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.09.001. Epub 2013 Sep 19. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 24056189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential value of LC-MS non-targeted metabonomics in the diagnosis of follicular thyroid carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 22;12:1076548. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1076548. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36620583 Free PMC article.
-
[Serum metabonomics study on Cr (Ⅵ ) subchronic exposure rats based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS platform].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2020 Mar 20;38(3):168-174. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121094-20190514-00199. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32306688 Chinese.
-
Bisallylic hydroxylation and epoxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by cytochrome P450.Lipids. 1996 Oct;31(10):1003-21. doi: 10.1007/BF02522457. Lipids. 1996. PMID: 8898299 Review.
References
-
- Jia Z., Guo Y., Lai H. Revealing the connotation of the “seven-seven” theory of Huangdi Neijing and the mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine intervention in elderly IVF-ET patients based on mitochondrial function. Chin. J. Exp. Herb. Med. 2023;29:28–134.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

