Hempseed Water-Soluble Protein Fraction and Its Hydrolysate Display Different Biological Features
- PMID: 40003634
- PMCID: PMC11856167
- DOI: 10.3390/life15020225
Hempseed Water-Soluble Protein Fraction and Its Hydrolysate Display Different Biological Features
Abstract
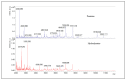
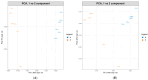
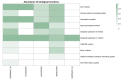
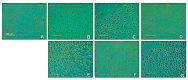
Hempseeds, from the Cannabis sativa plant, and its derivates are a versatile food option for various dietary preferences. Due to their aminoacidic profile, researchers have studied the presence of bioactive peptides in hempseed proteins. In this study, the water-soluble fraction of hempseed protein was extracted, and the derived peptides were analyzed. The investigation focused on their biological function, particularly their antioxidant activity. Several biological functions have arisen, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition activity, dipeptidyl-peptidase IV, dipeptidyl-peptidase III inhibition, and ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis activation. The hydrolysates show greater 2,2-azinobis-[3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid (ABTS) radical scavenging activity compared to the proteins (97.95 ± 4.48 versus 81.04 ± 10.63). Furthermore, the impact of these proteins and peptides on the U937 cell line was evaluated to assess cell viability and their potential role in modulating inflammation associated with gastrointestinal autoimmune diseases. Protein treatment resulted in a significant reduction in cell viability, as opposed to hydrolysates, which did not affect it.
Keywords: Cannabis sativa; IBD; MALDI-TOF; SDS-PAGE; antioxidant; autoimmune disease; hempseed; hempseeds hydrolysates; in vitro digestion; peptidomics; water-soluble protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exploration of Potentially Bioactive Peptides Generated from the Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Hempseed Proteins.J Agric Food Chem. 2017 Nov 29;65(47):10174-10184. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03590. Epub 2017 Nov 14. J Agric Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 29096438
-
Hempseed protein-derived short- and medium-chain peptides and their multifunctional properties.Adv Food Nutr Res. 2024;110:275-325. doi: 10.1016/bs.afnr.2024.01.002. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Adv Food Nutr Res. 2024. PMID: 38906589 Review.
-
Investigation on antioxidant, angiotensin converting enzyme and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory activity of Bambara bean protein hydrolysates.Food Chem. 2018 Jun 1;250:162-169. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.01.001. Epub 2018 Jan 2. Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 29412907
-
A review on the techno-functional, biological, and health-promoting properties of hempseed-derived proteins and peptides.J Food Biochem. 2022 Jul;46(7):e14127. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14127. Epub 2022 Mar 21. J Food Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35312074 Review.
-
The seed of industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.): Nutritional Quality and Potential Functionality for Human Health and Nutrition.Nutrients. 2020 Jun 29;12(7):1935. doi: 10.3390/nu12071935. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32610691 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preparation, Modification, Food Application, and Health Effects of Protein and Peptide from Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Seed: A Review of the Recent Literature.Foods. 2025 Mar 26;14(7):1149. doi: 10.3390/foods14071149. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40238243 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Callaway J.C. Hempseed as a Nutritional Resource: An Overview. Euphytica. 2004;140:65–72. doi: 10.1007/s10681-004-4811-6. - DOI
-
- Johnson R. Hemp as an Agricultural Commodity. Congressional Research Service; Washington, DC, USA: 2018.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

