Collagenase Clostridium Histolyticum Versus Percutaneous Needle Fasciotomy for Dupuytren's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40003669
- PMCID: PMC11856867
- DOI: 10.3390/life15020259
Collagenase Clostridium Histolyticum Versus Percutaneous Needle Fasciotomy for Dupuytren's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
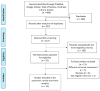
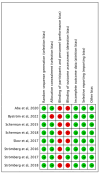
Minimally invasive treatments for Dupuytren's disease (DD), such as percutaneous needle fasciotomy (PNF) and collagenase clostridium histolyticum (CCH), have become alternatives to open surgeries. This meta-analysis compared these treatments in terms of complications, patient satisfaction, clinical outcomes, and recurrence. Relevant studies up to June 2024 were identified through major databases, following PRISMA guidelines, and the study was registered on PROSPERO. Statistical analysis using Review Manager 5.4 found PNF had lower post-operative rates of oedema (RR = 0.15, 95% CI [0.09, 0.27], p < 0.00001), lymphadenopathy (RR = 0.09, 95% CI [0.02, 0.38], p = 0.0010), and pruritus (RR = 0.1, 95% CI [0.01, 0.73], p = 0.02) compared to CCH. However, there were no significant differences in skin tears, recurrence, reintervention, extension deficit, or residual flexion at metacarpal and proximal interphalangeal joints (p > 0.05). Patient-reported outcomes, including QuickDASH and URAM scores, also showed no significant differences. Eleven studies involving 1443 patients were analysed, and most were at a low-to-moderate risk of bias, as assessed using the Cochrane or Newcastle-Ottawa tools. While PNF showed fewer minor complications, overall clinical and patient-reported outcomes were comparable between the treatments. These findings highlight the need to tailor treatment choices to patient preferences and clinical context.
Keywords: CCH; Dupuytren’s contracture; PNF; collagenase; percutaneous fasciotomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any potential conflicts of interest with respect to this manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Percutaneous Needle Fasciotomy versus Collagenase Injection for Dupuytren's Contracture: A Systematic Review of Comparative Studies.J Hand Microsurg. 2021 Jul;13(3):150-156. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1721876. Epub 2020 Dec 31. J Hand Microsurg. 2021. PMID: 34511831 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-Effectiveness and Patient Outcomes of Injectable Collagenase to Treat Dupuytren's Contracture.Cureus. 2021 Dec 20;13(12):e20530. doi: 10.7759/cureus.20530. eCollection 2021 Dec. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 35070563 Free PMC article.
-
Needle or Open Fasciotomy for Dupuytren’s Contracture: A Review of the Comparative Efficacy, Safety, and Cost-Effectiveness – An Update [Internet].Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2013 Nov 11. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2013 Nov 11. PMID: 24741726 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Dupuytren's Contracture Recurrence and Treatment Following Collagenase Clostridium Histolyticum Injection: A Longitudinal Assessment in a Veteran Population.Mil Med. 2023 Aug 29;188(9-10):e2975-e2981. doi: 10.1093/milmed/usad075. Mil Med. 2023. PMID: 36928340
-
Outcomes of limited fasciectomy, needle fasciotomy and collagenase injection for Dupuytren's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data.J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2025 Jul;50(7):878-890. doi: 10.1177/17531934251338349. Epub 2025 May 20. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2025. PMID: 40391547 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lermusiaux J., Debeyre N. L’Actualité Rhumatologique 1979 Présentée Aux Praticien. Expansion Scientifique Francaise; Paris, France: 1980.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

