Acute Kidney Injury in Patients After Cardiac Arrest: Effects of Targeted Temperature Management
- PMID: 40003674
- PMCID: PMC11856830
- DOI: 10.3390/life15020265
Acute Kidney Injury in Patients After Cardiac Arrest: Effects of Targeted Temperature Management
Abstract
Background: Cardiac arrest (CA) is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity, with survivors often developing post-cardiac arrest syndrome (PCAS), characterized by systemic inflammation, ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI), and multiorgan dysfunction. Acute kidney injury (AKI), a frequent complication, is associated with increased mortality and prolonged intensive care unit (ICU) stays. This study evaluates AKI incidence and progression in cardiac arrest patients managed with different temperature protocols and explores urinary biomarkers' predictive value for AKI risk.
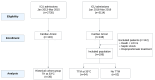
Methods: A prospective, single-center observational study was conducted, including patients with Return of Spontaneous Circulation (ROSC) post-cardiac arrest. Patients were stratified into three groups: therapeutic hypothermia (TH) at 33 °C, Targeted Temperature Management (TTM) at 35 °C, and no temperature management (No TTM). AKI was defined using KDIGO criteria, with serum creatinine and urinary biomarkers (TIMP-2 and IGFBP7) measured at regular intervals during ICU stay.
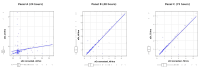
Results: AKI incidence at 72 h was 31%, varying across protocols. It was higher in the No TTM group at 24 h and in the TH and TTM groups during rewarming. Persistent serum creatinine elevation and fluid imbalance were notable in the TH group. Biomarkers indicated moderate tubular stress in the TTM and No TTM groups.
Conclusions: AKI is a frequent complication post-cardiac arrest, with the rewarming phase identified as critical for renal vulnerability. Tailored renal monitoring, biomarker-guided risk assessment, and precise temperature protocols are essential to improve outcomes.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; cardiac arrest; critical care; ischemia–reperfusion injury; renal outcomes; targeted temperature management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gräsner J.-T., Herlitz J., Tjelmeland I.B.M., Wnent J., Masterson S., Lilja G., Bein B., Böttiger B.W., Rosell-Ortiz F., Nolan J.P., et al. European Resuscitation Council Guidelines 2021: Epidemiology of Cardiac Arrest in Europe. Resuscitation. 2021;161:61–79. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2021.02.007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tsao C.W., Aday A.W., Almarzooq Z.I., Alonso A., Beaton A.Z., Bittencourt M.S., Boehme A.K., Buxton A.E., Carson A.P., Commodore-Mensah Y., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2022 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2022;145:e153–e639. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001052. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

