Effects of Exercise on Post-Stroke Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 40003693
- PMCID: PMC11857396
- DOI: 10.3390/life15020285
Effects of Exercise on Post-Stroke Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
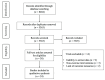
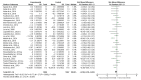
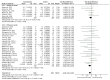
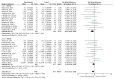
Numerous studies have investigated the effects of exercise on post-stroke depression (PSD), yet the findings remain inconclusive. This study aims to evaluate the impact of exercise on depressive symptoms in stroke patients and to identify the most effective exercise protocols for this population. A systematic review of the Embase, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and Scopus databases was conducted, with a search cutoff date of 13 September 2024. Quantitative synthesis was employed to assess the intervention effects, with effect sizes expressed as standardized mean differences (SMDs) and 95% confidence intervals to evaluate the efficacy of exercise in alleviating PSD. A total of 24 studies met the inclusion criteria. The results indicated that exercise significantly alleviated depressive symptoms in stroke patients (SMD = -0.18; p = 0.007). Specifically, multicomponent training emerged as the most effective intervention for reducing depression (SMD = -0.24; p = 0.008). Additionally, exercise programs with a duration of ≥12 weeks (SMD, -0.17; p = 0.04), ≥3 sessions per week (SMD, -0.20; p = 0.02), <60 min per session (SMD, -0.19; p = 0.05), and <180 min per week (SMD, -0.27; p = 0.02) were found to be the most effective in alleviating PSD. Exercise represents an effective strategy for managing PSD, with multicomponent training potentially serving as the optimal intervention. These findings provide evidence for clinicians, recommending that stroke patients engage in exercise at least three times weekly, with individual sessions not exceeding 60 min. By increasing the frequency of exercise, the cumulative weekly time should ideally remain below 180 min for optimal outcomes.
Keywords: exercise; multicomponent training; post-stroke depression; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Putra K.A.N., Suyasa I.G.P.D., Kamaryati N.P., Dharmapatni N.W.K. Development of a self-care guideline to prevent rehospitalization in stroke patients: A modified Delphi study. J. Ners. 2024;19:p21. doi: 10.20473/jn.v19i1.48937. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

