The Gut Bacteria of Gampsocleis gratiosa (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae) by Culturomics
- PMID: 40003753
- PMCID: PMC11857073
- DOI: 10.3390/insects16020123
The Gut Bacteria of Gampsocleis gratiosa (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae) by Culturomics
Abstract
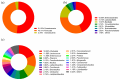
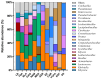
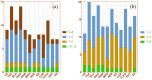
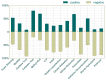
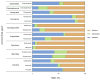
Gampsocleis gratiosa Brunner von Wattenwyl, 1862, is a type of omnivorous chirping insect with a long history of artificial breeding. It has high economic value and is also an excellent orthopteran model organism. In this study, 12 types of culture media combined with 16S rRNA sequencing were employed to isolate 838 bacterial strains from the gut of G. gratiosa. After sequence comparison, a total of 98 species of bacteria were identified, belonging to 3 phyla, 5 classes, 11 orders, 20 families, and 45 genera. Firmicutes and Proteobacteria accounted for the majority (92.86%). At the order level, Enterobacteriaceae, Bacillales, and Lactobacillales predominated (79.59%). At the genus level, Klebsiella (11.22%) and Enterococcus (7.14%) predominated. This study also enumerated the strain morphological, physiological and biochemical properties of 98 species of bacteria, including colony morphology, Gram staining, bacterial motility test, temperature gradient growth, pH gradient growth, citrate utilization test, temperature oxidase test, contact enzyme test, methyl red test, V-P test, indole test, gelatin liquefaction test, nitrate reduction test, hydrogen sulfide test, starch hydrolysis test, cellulose decomposition test, esterase (corn oil) test and antibiotic susceptibility testing. Additionally, 16 antibiotics were utilized to test the bacterial susceptibility of the strains. This study explored the types and community structure of some culturable microorganisms in the intestinal tract of G. gratiosa and recorded their physiological characteristics. These data reflect the physiological functions of the intestinal microorganisms of G. gratiosa and provide support for subsequent research on the interaction mechanism between microorganisms and their hosts.
Keywords: Gampsocleis gratiosa; culturomics; gut bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bacterial Communities in the Feces of Laboratory Reared Gampsocleis gratiosa (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae) across Different Developmental Stages and Sexes.Insects. 2022 Apr 7;13(4):361. doi: 10.3390/insects13040361. Insects. 2022. PMID: 35447806 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of the acrosome complex in the bush cricket Gampsocleis gratiosa (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae).Arthropod Struct Dev. 2017 Jul;46(4):579-587. doi: 10.1016/j.asd.2017.01.002. Epub 2017 Mar 3. Arthropod Struct Dev. 2017. PMID: 28115255
-
Establishment and characterization of an embryonic cell line from Gampsocleis gratiosa (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae).In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2011 Apr;47(4):327-32. doi: 10.1007/s11626-011-9397-4. Epub 2011 Mar 18. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2011. PMID: 21424241
-
Culturing Bacteria From Fermentation Pit Muds of Baijiu With Culturomics and Amplicon-Based Metagenomic Approaches.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jun 23;11:1223. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01223. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32714285 Free PMC article.
-
[Construction of gut microbial culture banks: advances, methods and perspectives].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2023 Nov 25;39(11):4463-4481. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.230026. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 38013178 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Insight into the Microbiota of Orthopteran in Relation to Gut Compartmentalisation.Insects. 2025 May 24;16(6):555. doi: 10.3390/insects16060555. Insects. 2025. PMID: 40558985 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhou Z., Kou X., Qian L., Liu J. Transcriptome profile of Chinese bush cricket, Gampsocleis gratiosa: A resource for microsatellite marker development. Entomol. Res. 2016;46:197–205. doi: 10.1111/1748-5967.12165. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

