Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Phosphate Transporter Gene Family in Zea mays Under Phosphorus Stress
- PMID: 40003911
- PMCID: PMC11855068
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26041445
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Phosphate Transporter Gene Family in Zea mays Under Phosphorus Stress
Abstract
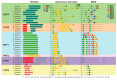
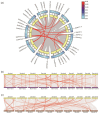
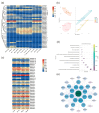
Phosphorus is one of the key limiting factors for maize growth and productivity, and low-phosphorus stress severely restricts crop yield and stability. Enhancing the ability of maize to grow under low-phosphorus stress and improving phosphorus use efficiency (PUE) are crucial for achieving high and stable yields. Phosphate transporter (PHT) family proteins play a crucial role in the absorption, transport, and utilization of phosphorus in plants. In this study, we systematically identified the PHT gene family in maize, followed by the phylogenetic, gene structure, and expression profiles. The results show that these genes are widely distributed across the 10 chromosomes of maize, forming multiple subfamilies, with the PHT1 subfamily having the largest number. Cis-regulatory element analysis revealed that these genes might play key roles in plant stress responses and hormone regulation. Transcriptome analysis under phosphorus-deficient and normal conditions demonstrated developmental stage- and tissue-specific expression patterns, identifying candidate genes, such as ZmPHT1-3, ZmPHT1-4, ZmPHT1-10, and ZmPHO1-H3, involved in phosphorus stress response. This study presents a comprehensive and systematic analysis of the PHT gene family in maize, providing key molecular resources for improving phosphorus use efficiency and breeding phosphorus-efficient maize varieties.
Keywords: PHT family; low-phosphorus stress; maize; stress responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification, expression analysis, and response to abiotic stress of the phosphate transporter gene family in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.).BMC Plant Biol. 2025 May 21;25(1):677. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06720-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40399819 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Identification, Evolution and Expression Analysis of the Zea mays PHT1 Gene Family Reveals Several New Members Involved in Root Colonization by Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 13;17(6):930. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060930. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27304955 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Expression Profiling of the Cytokinin Synthesis Gene Family IPT in Maize.Genes (Basel). 2025 Mar 31;16(4):415. doi: 10.3390/genes16040415. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40282375 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Assessment for the Phosphate Transporter 2 Gene Family Within Sweet Potato Under Phosphorus Deficiency Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 17;26(6):2681. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062681. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141323 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfur and phosphorus transporters in plants: Integrating mechanisms for optimized nutrient supply.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2025 Jul;224:109918. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2025.109918. Epub 2025 Apr 11. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40239245 Review.
References
-
- Oukaltouma K., Moukhtari A.E., Lahrizi Y., Mouradi M., Farissi M., Willems A., Qaddoury A., Bekkaoui F., Ghoulam C. Phosphorus deficiency enhances water deficit impact on some morphological and physiological traits in four faba bean (Vicia faba L.) varieties. Ital. J. Agron. 2021;16:1662. doi: 10.4081/ija.2020.1662. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

