Early Intervention in Herpes Simplex Virus-1 Replication in Vitro with Allenic Macrolide Archangiumide
- PMID: 40004002
- PMCID: PMC11855526
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26041537
Early Intervention in Herpes Simplex Virus-1 Replication in Vitro with Allenic Macrolide Archangiumide
Abstract
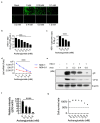
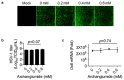
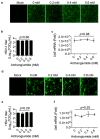
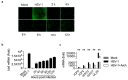
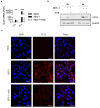
Archangiumide is a unique macrolide natural product that features an endocyclic allene functionality, rendering it a prototype of a new class of secondary metabolites of microbial origin. However, its biological and/or pharmaceutical roles remain obscure. In this study, we have unveiled an antiviral potency of archangiumide that was effective against herpes simplex virus (HSV-1) replication. We found that archangiumide did not affect host cell viability, nor pathogen infectivity, but suppressed HSV-1 early replication, in terms of early replication genes, such as ICP0, ICP4, etc. Further scrutinizing the underlined master regulator, we found that HSV-1 VP16 protein expression was inhibited by archangiumide, as well as VP16 nuclear translocation. As VP16 is a coactivator of transcription, archangiumide harnessed the master regulator of HSV-1 early replication. Together, here we provide evidence that allene macrolide archangiumide possesses robust antiviral functions that may be valuable for a novel viral infection intervention, as macrolides are generally safe drugs for prolonged treatments.
Keywords: HSV-1; antiviral; archangiumide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hu J.-Q., Wang J.-J., Li Y.-L., Zhuo L., Zhang A., Sui H.-Y., Li X.-J., Shen T., Yin Y., Wu Z.-H., et al. Combining NMR-Based Metabolic Profiling and Genome Mining for the Accelerated Discovery of Archangiumide, an Allenic Macrolide from the Myxobacterium Archangium violaceum SDU8. Org. Lett. 2021;23:2114–2119. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c00265. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

