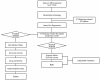
A Novel Prognostic Signature of Mitophagy-Related E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 40004017
- PMCID: PMC11855622
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26041551
A Novel Prognostic Signature of Mitophagy-Related E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Breast Cancer
Abstract
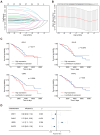
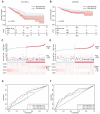
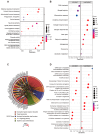
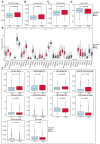
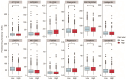
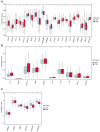
Mitophagy plays a critical role in maintaining mitochondrial quality and cellular homeostasis. But the specific contribution of mitophagy-related E3 ubiquitin ligases to prognoses remains largely unexplored. In this study, we identified a novel mitophagy-related E3 ubiquitin ligase prognostic signature using least absolute shrinkage and selector operator (LASSO) and multivariate Cox regression analyses in breast cancer. Based on median risk scores, patients were divided into high-risk and low-risk groups. Functional enrichment analyses were conducted to explore the biological differences between the two groups. Immune infiltration, drug sensitivity, and mitochondrial-related phenotypes were also analyzed to evaluate the clinical implications of the model. A four-gene signature (ARIH1, SIAH2, UBR5, and WWP2) was identified, and Kaplan-Meier analysis demonstrated that the high-risk group had significantly worse overall survival (OS). The high-risk patients exhibited disrupted mitochondrial metabolism and immune dysregulation with upregulated immune checkpoint molecules. Additionally, the high-risk group exhibited higher sensitivity to several drugs targeting the Akt/PI3K/mTORC1 signaling axis. Accompanying mitochondrial metabolic dysregulation, mtDNA stress was elevated, contributing to activation of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) in the high-risk group. In conclusion, the identified signature provides a robust tool for risk stratification and offers insights into the interplay between mitophagy, immune modulation, and therapeutic responses for breast cancer.
Keywords: E3 ubiquitin ligase; breast cancer; immune; metabolic; mitophagy; prognostic signature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrative analysis of the prognostic value and immune microenvironment of mitophagy-related signature for multiple myeloma.BMC Cancer. 2023 Sep 12;23(1):859. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11371-7. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37700273 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of a circRNA-regulated E3 ubiquitin ligase signature and nomogram to predict immunotherapeutic efficacy and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jun 10;29(1):318. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01893-6. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38858746 Free PMC article.
-
A mitophagy-related gene signature associated with prognosis and immune microenvironment in colorectal cancer.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 4;12(1):18688. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23463-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36333388 Free PMC article.
-
PINK1 and Parkin: team players in stress-induced mitophagy.Biol Chem. 2020 May 26;401(6-7):891-899. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2020-0135. Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32297878 Review.
-
Functional significance and therapeutic implication of ring-type E3 ligases in colorectal cancer.Oncogene. 2018 Jan 11;37(2):148-159. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.313. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 28925398 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Onkar S.S., Carleton N.M., Lucas P.C., Bruno T.C., Lee A.V., Vignali D.A.A., Oesterreich S. The Great Immune Escape: Understanding the Divergent Immune Response in Breast Cancer Subtypes. Cancer Discov. 2023;13:23–40. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-0475. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

