APOBEC3-Related Editing and Non-Editing Determinants of HIV-1 and HTLV-1 Restriction
- PMID: 40004025
- PMCID: PMC11855278
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26041561
APOBEC3-Related Editing and Non-Editing Determinants of HIV-1 and HTLV-1 Restriction
Abstract
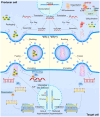
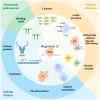
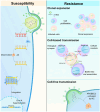
The apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme catalytic polypeptide-like 3 (APOBEC3/A3) family of cytosine deaminases serves as a key innate immune barrier against invading retroviruses and endogenous retroelements. The A3 family's restriction activity against these parasites primarily arises from their ability to catalyze cytosine-to-uracil conversions, resulting in genome editing and the accumulation of lethal mutations in viral genomes. Additionally, non-editing mechanisms, including deaminase-independent pathways, such as blocking viral reverse transcription, have been proposed as antiviral strategies employed by A3 family proteins. Although viral factors can influence infection progression, the determinants that govern A3-mediated restriction are critical in shaping retroviral infection outcomes. This review examines the interactions between retroviruses, specifically human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and human T-cell leukemia virus type 1, and A3 proteins to better understand how editing and non-editing activities contribute to the trajectory of these retroviral infections.
Keywords: APOBEC3 family proteins; HIV-1; HTLV-1; deaminase-dependent mechanisms; deaminase-independent mechanisms; retrovirus restriction.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could produce a potential conflict of interest as related to this research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
APOBEC3 degradation is the primary function of HIV-1 Vif determining virion infectivity in the myeloid cell line THP-1.mBio. 2023 Aug 31;14(4):e0078223. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00782-23. Epub 2023 Aug 9. mBio. 2023. PMID: 37555667 Free PMC article.
-
APOBEC3A, APOBEC3B, and APOBEC3H haplotype 2 restrict human T-lymphotropic virus type 1.J Virol. 2012 Jun;86(11):6097-108. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06570-11. Epub 2012 Mar 28. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22457529 Free PMC article.
-
Antiretroviral APOBEC3 cytidine deaminases alter HIV-1 provirus integration site profiles.Nat Commun. 2023 Jan 10;14(1):16. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35379-y. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36627271 Free PMC article.
-
APOBEC3 proteins and reverse transcription.Virus Res. 2008 Jun;134(1-2):74-85. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2007.12.022. Epub 2008 Feb 11. Virus Res. 2008. PMID: 18262674 Review.
-
Unmasking immune sensing of retroviruses: interplay between innate sensors and host effectors.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014 Dec;25(6):657-68. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014. PMID: 25240798 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

