Chronic Kidney Disease and Osteoarthritis: Current Understanding and Future Research Directions
- PMID: 40004032
- PMCID: PMC11854965
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26041567
Chronic Kidney Disease and Osteoarthritis: Current Understanding and Future Research Directions
Abstract
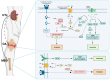
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a significant public health concern. Osteoarthritis (OA), a common form of arthritis, has been shown to have a dramatically increased prevalence, particularly among individuals aged 40-50 and older, in the presence of CKD. Furthermore, CKD may exacerbate the progression and impact of OA. A survey study revealed that 53.9% of CKD patients undergoing long-term hemodialysis were diagnosed with OA. These findings underscore the potential association between CKD and OA. Uremic toxins, such as indoxyl sulfate, p-cresyl sulfate, transforming growth factor-β, and advanced glycation end-products, are regarded as potential risk factors in various CKD-related conditions, affecting bone and joint metabolism. However, whether these factors serve as a bridging mechanism between CKD and OA comorbidities, as well as their detailed roles in this context, remains unclear. Addressing the progression of OA in CKD patients and identifying effective treatment and prevention strategies is an urgent challenge that warrants immediate attention. This review focuses on describing and discussing the molecular pathological mechanisms underlying CKD-associated OA and the possible therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: calcium; chronic kidney disease; iron; osteoarthritis; uremic toxins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- United States Renal Data System . USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. National Institutes of Health; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; Bethesda, MD, USA: 2024.
-
- Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database . 2023 NHIRD Annual Statistical Report. National Health Insurance Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare; Taipei, Taiwan: 2023.
-
- Aguilar A., Gifre L., Ureña-Torres P., Carrillo-López N., Rodriguez-García M., Massó E., da Silva I., López-Báez V., Sánchez-Bayá M., Prior-Español Á. Pathophysiology of bone disease in chronic kidney disease: From basics to renal osteodystrophy and osteoporosis. Front. Physiol. 2023;14:1177829. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1177829. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

