Role of Melatonin in Regulating Rat Skeletal Muscle Tissue Inflammation and Damage Following Carbon Tetrachloride Intoxication
- PMID: 40004180
- PMCID: PMC11855742
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26041718
Role of Melatonin in Regulating Rat Skeletal Muscle Tissue Inflammation and Damage Following Carbon Tetrachloride Intoxication
Abstract
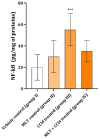
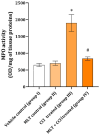
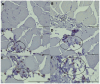
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is a toxic compound that causes severe oxidative stress and inflammation in skeletal muscles, resulting in structural damage, mitochondrial dysfunction, and impaired contractile function. While CD45 and melatonin (MLT) are implicated in immune modulation and antioxidative defense, their precise roles in mitigating CCl4-induced muscle damage remain incompletely understood, warranting further investigation. This study used 24 Wistar rats divided into four groups to evaluate the effects of MLT on CCl4-induced muscle inflammation. The first group was used as a control group, the second received only MLT (50 mg/kg), and the third group received CCl4, while the fourth group received MLT (50 mg/kg) and CCl4. Muscle tissues, obtained 24 h after the commencement of the experiment, were analyzed using biochemical assays for inflammatory markers, histological staining, and immunohistochemistry to assess structural and cellular changes. CCl4 exposure significantly increased NF-κB activity, nitric oxide levels, iNOS expression, and CD45-positive immune cell infiltration in skeletal muscles, indicating heightened inflammation and oxidative stress. Pretreatment with MLT markedly reduced these inflammatory markers, restoring damaged tissue and diminishing immune cell infiltration. Histological analyses confirmed reduced inflammatory cell presence and tissue damage in MLT-treated animals, highlighting its protective effects. Melatonin demonstrates significant protective effects against CCl4-induced skeletal muscle damage by reducing inflammation, oxidative stress, and immune cell infiltration, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent.
Keywords: CCl4; CD45; inflammation; nitric oxide; skeletal muscles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Melatonin modulates acute cardiac muscle damage induced by carbon tetrachloride - involvement of oxidative damage, glutathione, and arginine and nitric oxide metabolism.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021 Apr;99(4):360-367. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2020-0201. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32758112
-
Pre- vs. post-treatment with melatonin in CCl4-induced liver damage: Oxidative stress inferred from biochemical and pathohistological studies.Life Sci. 2018 Jun 1;202:28-34. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.04.003. Epub 2018 Apr 4. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29626529
-
Melatonin attenuates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal injury by reducing oxidative stress, iNOS, MAPK, and NF-kB expression.J Endourol. 2009 Jul;23(7):1165-73. doi: 10.1089/end.2009.0035. J Endourol. 2009. PMID: 19530942
-
Curcumin protects against acute liver damage in the rat by inhibiting NF-kappaB, proinflammatory cytokines production and oxidative stress.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Jun;1770(6):989-96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2007.02.004. Epub 2007 Feb 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17383825
-
Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effect of melatonin on recovery from muscular trauma induced in rats.Exp Mol Pathol. 2019 Feb;106:52-59. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2018.12.001. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30521792
References
-
- Lilić M.L., Toskić D., Stefanović R.Ž., Mekić B.B., Ilić I.R., Stojanović N.M. The role of mast cells in carbon tetrachloride induced rat skeletal muscle tissue damage. Acta Medica Median. 2019;58:11–15. doi: 10.5633/amm.2019.0202. - DOI
-
- Sokolović D.T., Lilić L., Milenković V., Stefanovic R., Ilic Popovic T., Mekic B., Ilić I., Stojanović N.M., Ilić I.R. Effects of melatonin on oxidative stress parameters and pathohistological changes in rat skeletal muscle tissue following carbon tetrachloride application. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018;26:1044–1050. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2018.05.013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ničković V.P., Novaković T., Lazarević S., Šulović L., Živković Z., Živković J., Mladenović B., Stojanović N.M., Petrović V., Sokolović D.T. Pre- vs. post-treatment with melatonin in CCl4-induced liver damage: Oxidative stress inferred from biochemical and pathohistological studies. Life Sci. 2018;202:28–34. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.04.003. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

