High-Level Lanthanide-Doped Upconversion Nanoparticles-Based Aptasensor to Increase Carcinoembryonic Antigen Detection Sensitivity
- PMID: 40004320
- PMCID: PMC11857722
- DOI: 10.3390/ma18040796
High-Level Lanthanide-Doped Upconversion Nanoparticles-Based Aptasensor to Increase Carcinoembryonic Antigen Detection Sensitivity
Abstract
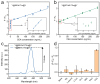
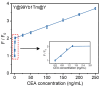
Boosting the accuracy and speed of cancer detection is highly desirous in tumor detection, and sensors capable of detecting carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) have great application prospects in this field. A highly sensitive sensor is constructed based on the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) with heavily rare-earth-doped upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) as energy donors and polydopamine nanoparticles (PDA NPs) as energy acceptors. This sensor detects the fluctuations in CEA molecules via luminescence quenching and recovery resulting from a competitive binding assay between CEA and PDA NPs. The high-level-doped design of UCNPs (i.e., NaYF4@NaYbF4:1%Tm@NaYF4) is beneficial, providing upconversion luminescence intensity that is more than 10 times higher than that of the conventional low-level-doped UCNPs (i.e., NaYF4@NaYF4:20%Yb, 0.2%Tm@NaYF4). The sensor exhibits impressive sensitivity. Specifically, in diluted fetal bovine serum, the detection limit reaches 0.013 ng/mL in the range of 0-1.5 ng/mL (S/N = 3), while the detection limit is 1.38 ng/mL in the range of 1.5-250 ng/mL (S/N = 3). This method has great potential for future applications in the rapid and early diagnosis and treatment of cancer.
Keywords: CEA detection; FRET; UCNPs-PDA NP sensor; high-level doping.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Lu Xia and Xingyu Liu are employed by the company The 49th Research Institute of China Electronics Technology Group Corporation. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Tommasi M., Pieroni C., Cappelli G. Radioimmunoassay of carcinoembryonic antigen: Observations and methodological variations. J. Nucl. Med. Allied. Sci. 1978;22:163–167. - PubMed
-
- Schiedeck T.H.K., Wellm C., Roblick U.J., Broll R., Bruch H.P. Diagnosis and monitoring of colorectal cancer by L6 blood serum polymerase chain reaction is superior to carcinoembryonic antigen-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Dis. Colon. Rectum. 2003;46:818–825. doi: 10.1007/s10350-004-6662-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huang J., Jiao L., Xu W., Fang Q., Wang H., Cai X., Yan H., Gu W., Zhu C. Immobilizing enzymes on noble metal hydrogel nanozymes with synergistically enhanced peroxidase activity for ultrasensitive immunoassays by cascade signal amplification. ACS Appl. Mater. 2021;13:33383–33391. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c09100. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

