Type 1 Diabetes Risk Variants Reduce Beta Cell Function
- PMID: 40004501
- PMCID: PMC11855905
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16020172
Type 1 Diabetes Risk Variants Reduce Beta Cell Function
Abstract
Introduction: The variants rs10517086 and rs1534422 are predictive of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) development and poor residual β cell function within the first year of diagnosis. However, the mechanism by which risk is conferred is unknown. We explored the impact of both variants on β cell function in vitro and assessed their relationship with C-peptide in people with T1DM and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
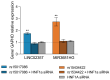
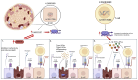
Methods: Using CRISPR/Cas9, the variants were introduced into a β cell line (BRIN-BD11) and a T cell line (Jurkat cells) from which the conditioned media was applied to otherwise healthy β cells to model the inflammatory environment associated with these variants.
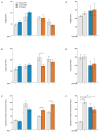
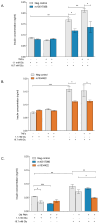
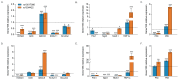
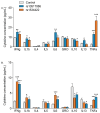
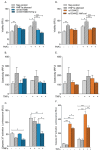
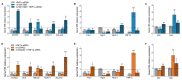
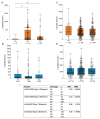
Results: Both variants significantly reduced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reduced expression of several β cell markers and transcription factors (KCNJ11, KCNQ1, SCL2A2, GCK, NKX6.1, Pdx1 NGN3). However, HNF1A was significantly upregulated in the presence of both variants. We subsequently silenced HNF1A in variant expressing BRIN-BD11 cells using siRNA and found that gene expression profiles were normalised. Induction of each variant significantly increased expression of the lncRNAs they encode, which was normalised upon HNF1A silencing. Analysis of the DARE (Diabetes Alliance for Research in England) study revealed an association of rs10517086_A genotype with C-peptide in 153 individuals with T1DM, but not in 417 people with T2DM.
Conclusions: These data suggest that rs1534422 and rs10517086 exert multiple insults on the β cell through excessive upregulation of HNF1A and induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and highlight their utility as prognostic markers of β cell function.
Keywords: inflammation; risk variants; type 1 diabetes; β cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A20 controls expression of beta-cell regulatory genes and transcription factors.J Mol Endocrinol. 2021 Sep 28;67(4):189-201. doi: 10.1530/JME-21-0076. J Mol Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34463643
-
Lower Circulating miR-122 Level in Patients with HNF1A Variant-Induced Diabetes Compared with Type 2 Diabetes.J Diabetes Res. 2018 Aug 1;2018:7842064. doi: 10.1155/2018/7842064. eCollection 2018. J Diabetes Res. 2018. PMID: 30155490 Free PMC article.
-
Human islets expressing HNF1A variant have defective β cell transcriptional regulatory networks.J Clin Invest. 2019 Jan 2;129(1):246-251. doi: 10.1172/JCI121994. Epub 2018 Dec 3. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 30507613 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of HNF1α and HNF4α in pancreatic β-cells: lessons from a monogenic form of diabetes (MODY).Vitam Horm. 2014;95:407-23. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800174-5.00016-8. Vitam Horm. 2014. PMID: 24559927 Review.
-
Regulation of insulin synthesis and secretion and pancreatic Beta-cell dysfunction in diabetes.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2013 Jan 1;9(1):25-53. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2013. PMID: 22974359 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

