Chemical Evolution of Life on Earth
- PMID: 40004549
- PMCID: PMC11854950
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16020220
Chemical Evolution of Life on Earth
Abstract
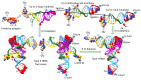
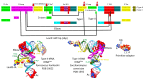
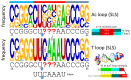
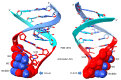
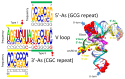
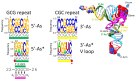
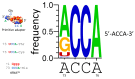
Background/Objectives: The origin of genes and genetics is the story of the coevolution of translation systems and the genetic code. Remarkably, the history of the origin of life on Earth was inscribed and preserved in the sequences of tRNAs. Methods: Sequence logos demonstrate the patterning of pre-life tRNA sequences. Results: The pre-life type I and type II tRNA sequences are known to the last nucleotide with only a few ambiguities. Type I and type II tRNAs evolved from ligation of three 31 nt minihelices of highly patterned and known sequence followed by closely related 9 nt internal deletion(s) within ligated acceptor stems. The D loop 17 nt core was a truncated UAGCC repeat. The anticodon and T 17 nt stem-loop-stems are homologous sequences with 5 nt stems and 7 nt U-turn loops that were selected in pre-life to resist ribozyme nucleases and to present a 3 nt anticodon with a single wobble position. The 7 nt T loop in tRNA was selected to interact with the D loop at the "elbow". The 5'-acceptor stem was based on a 7 nt truncated GCG repeat. The 3'-acceptor stem was based on a complementary 7 nt CGC repeat. In pre-life, ACCA-Gly was a primitive adapter molecule ligated to many RNAs, including tRNAs, to synthesize polyglycine. Conclusions: Analysis of sequence logos of tRNAs from an ancient Archaeon substantiates how the pre-life to life transition occurred on Earth. Polyglycine is posited to have aggregated complex molecular assemblies, including minihelices, tRNAs, cooperating molecules, and protocells, leading to the first life on Earth.
Keywords: anticodon; chemical evolution; genetic code; last universal common (cellular) ancestor; minihelices; origin of life; polyglycine; pre-life; tRNA; type II tRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
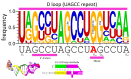







Similar articles
-
tRNA structure and evolution and standardization to the three nucleotide genetic code.Transcription. 2017 Aug 8;8(4):205-219. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2017.1318811. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Transcription. 2017. PMID: 28632998 Free PMC article.
-
Type-II tRNAs and Evolution of Translation Systems and the Genetic Code.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 22;19(10):3275. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103275. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30360357 Free PMC article.
-
tRNA evolution from the proto-tRNA minihelix world.Transcription. 2016 Oct 19;7(5):153-163. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2016.1235527. Transcription. 2016. PMID: 27636862 Free PMC article.
-
The 3 31 Nucleotide Minihelix tRNA Evolution Theorem and the Origin of Life.Life (Basel). 2023 Nov 19;13(11):2224. doi: 10.3390/life13112224. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of Life on Earth: tRNA, Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases and the Genetic Code.Life (Basel). 2020 Mar 2;10(3):21. doi: 10.3390/life10030021. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32131473 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lei L., Burton Z.F. Origin of Type II tRNA Variable Loops, Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase Allostery from Distal Determinants, and Diversification of Life. DNA. 2024;4:252–275. doi: 10.3390/dna4030017. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

