Developmental Expression Patterns of miRNA in Mythimna separata Walker (Lepidotera: Noctuidae)
- PMID: 40004562
- PMCID: PMC11855462
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16020234
Developmental Expression Patterns of miRNA in Mythimna separata Walker (Lepidotera: Noctuidae)
Abstract
Background/objectives: miRNAs are a family of single-stranded non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression by targeting messenger RNAs (mRNAs) for suppression, with an average length of 22 nt. The oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata Walker, is a pest insect with long-distance migratory capability, which causes severe loss of grains and pastures in Eastern Asia, Southeastern Asia, and Oceania. This study aims to elucidate the post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms of miRNAs in the development of this pest.
Methods: We carried out small RNA sequencing on samples from eggs, third instar larvae, pre-pupae, pupae, and adults.
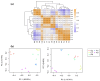
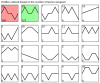
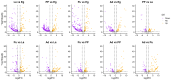
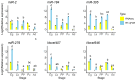
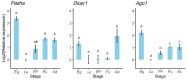
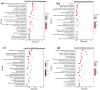
Results: A total of 400 miRNAs were identified, among which 40 were known and 360 were novel miRNAs. Dynamic trend analysis of miRNAs revealed that 199 miRNAs were highly expressed in eggs (profile 12), while 173 miRNAs were highly expressed in both eggs and pupae (profile 13). The results of differential expression analysis of miRNAs (DEmiR) revealed that 75 miRNAs were significantly more abundant in eggs compared to other developmental stages. Furthermore, more up-regulated miRNAs were observed than down-regulated miRNAs in adults relative to 3rd instar larvae, pre-pupae, and pupae. The core genes for miRNA biosynthesis-Pasha, Dicer1, and Ago1-were highly expressed in eggs but poorly expressed in 3rd instar larvae. KEGG enrichment analyses indicated that several genes in the pentose and glucuronate interconversion pathway, as well as the fructose and mannose metabolism pathway, were regulated by DEmiRs.
Conclusions: DEmiRNAs targeted most genes of M. separata, resulting in a complex miRNA-mRNA regulation mode.
Keywords: armyworm; development; migratory insect; small RNA sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
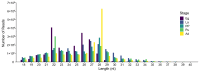
Similar articles
-
Identification and developmental profiling of microRNAs in diamondback moth, Plutellaxylostella (L.).PLoS One. 2013 Nov 13;8(11):e78787. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078787. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24236051 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Prediction of Differentially Expressed MicroRNAs Associated with Detoxification Pathways in Larvae of Spodoptera frugiperda.Genes (Basel). 2024 Aug 3;15(8):1021. doi: 10.3390/genes15081021. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202382 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of DNA methyltransferase 1 and its role in temperature change of armyworm Mythimna separata Walker.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2020 Apr;103(4):e21651. doi: 10.1002/arch.21651. Epub 2020 Jan 13. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31943343
-
Deep sequencing of small RNA libraries reveals dynamic regulation of conserved and novel microRNAs and microRNA-stars during silkworm development.BMC Genomics. 2010 Jan 20;11:52. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-52. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20089182 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of microRNAs from Plutella xylostella larvae associated with parasitization by Diadegma semiclausum.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Apr;43(4):309-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2013.01.004. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23352895 Review.
References
-
- Jagadeeswaran G., Zheng Y., Sumathipala N., Jiang H., Arrese E.L., Soulages J.L., Zhang W., Sunkar R. Deep sequencing of small RNA libraries reveals dynamic regulation of conserved and novel microRNAs and microRNA-stars during silkworm development. BMC Genom. 2010;11:52. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-52. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

