Advances in Biologic Therapies for Allergic Diseases: Current Trends, Emerging Agents, and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 40004611
- PMCID: PMC11856668
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14041079
Advances in Biologic Therapies for Allergic Diseases: Current Trends, Emerging Agents, and Future Perspectives
Abstract
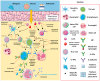
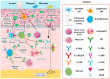
Biologic therapies have revolutionized the treatment of severe allergic diseases, including asthma, atopic dermatitis (AD), chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU), chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP), eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases (EGIDs), and allergic rhinitis (AR). These molecularly targeted agents provide significant benefits for patients unresponsive to conventional treatments by addressing underlying immune mechanisms, particularly type 2 inflammation driven by cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. Recent advancements include biologics targeting alarmins like thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and IL-33, which may address both type 2 and non-type 2 inflammation, broadening their therapeutic scope. Despite their effectiveness, biologics remain expensive, posing socioeconomic challenges, and there are concerns regarding long-term safety and inter-individual variability in responses. Promising innovations such as bispecific antibodies and ultra-long-acting agents are under investigation, alongside digital health tools like remote biomarker monitoring and AI-driven decision support systems, which aim to enhance personalized care. However, disparities in access, particularly for underserved populations, underscore the need for policy reforms and affordable biosimilars. This review synthesizes recent findings and emerging trends, highlighting the evolving role of biologics in transforming allergic disease management and offering insights into future research directions.
Keywords: allergic rhinitis; allergy; asthma; atopic dermatitis; biologics; chronic rhinosinusitis; cytokines; monoclonal antibodies; spontaneous urticaria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shin Y.H., Hwang J., Kwon R., Lee S.W., Kim M.S., GBD 2019 Allergic Disorders Collaborators. Shin Y.H., Hwang J., Kwon R., Lee S.W., et al. Global, regional, and national burden of allergic disorders and their risk factors in 204 countries and territories, from 1990 to 2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Allergy. 2023;78:2232–2254. doi: 10.1111/all.15807. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dierick B.J.H., van der Molen T., Flokstra-de Blok B.M.J., Muraro A., Postma M.J., Kocks J.W.H., van Boven J.F. Burden and socioeconomics of asthma, allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis and food allergy. Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 2020;20:437–453. doi: 10.1080/14737167.2020.1819793. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

