Vaccine-Based Immunotherapy for Oropharyngeal and Nasopharyngeal Cancers
- PMID: 40004705
- PMCID: PMC11856027
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14041170
Vaccine-Based Immunotherapy for Oropharyngeal and Nasopharyngeal Cancers
Abstract
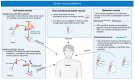
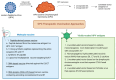
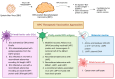
Viral infections such as human papillomavirus (HPV) and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) play a critical role in the onset of oropharyngeal (OPC) and nasopharyngeal cancer (NPC), respectively. Despite advancements in targeted therapies and immunotherapies, in the recurrent/metastatic setting, these tumors remain incurable diseases with poor prognosis. The development of therapeutic tumor vaccines, utilizing either neoantigens or oncoviral antigens, represents a promising addition to the cancer immunotherapy arsenal. Research on vaccine-based immunotherapy for OPC and NPC focuses on targeting viral antigens, particularly HPV E6/E7 and EBV EBNA1/LMP2. The potential for vaccine platforms, including peptide-based, DNA, RNA, and viral vector-based vaccines, to induce durable immune responses against viral antigens is reported. The early-phase clinical trials evaluating vaccine-based therapies for HPV-related OPC and EBV-related NPC revealed safety and preliminary signs of efficacy; however, further clinical trials are crucial for validation. This review provides an overview of the current landscape of vaccine-based strategies for HPV-related OPC and EBV-related NPC, discussing their biological mechanisms and immune processes involved in anti-HPV and anti-EBV vaccine treatments, with a particular focus on the immune factors that influence these therapies.
Keywords: immunotherapy; nasopharynx; oropharynx; vaccines; virus-related head and neck cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical presentation and outcome of human papillomavirus-positive nasopharyngeal carcinoma in a North American cohort.Cancer. 2022 Aug 1;128(15):2908-2921. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34266. Epub 2022 May 19. Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35588085
-
Epstein-Barr virus and human papillomavirus infections and genotype distribution in head and neck cancers.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 18;9(11):e113702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113702. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25405488 Free PMC article.
-
Aerodigestive cancers: pharyngeal cancer.FP Essent. 2014 Sep;424:18-25. FP Essent. 2014. PMID: 25198383
-
Epstein-Barr virus-infected nasopharyngeal carcinoma therapeutics: oncoprotein targets and clinical implications.Med Oncol. 2025 Jan 31;42(3):59. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02610-x. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39888474 Review.
-
Epstein Barr Virus: Development of Vaccines and Immune Cell Therapy for EBV-Associated Diseases.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 8;12:734471. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.734471. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34691042 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Update: Immunotherapeutic Strategies in HPV-Associated Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Viruses. 2025 May 16;17(5):712. doi: 10.3390/v17050712. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40431723 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources