Advancements in Diagnostic Methods and Imaging Technologies in Dentistry: A Literature Review of Emerging Approaches
- PMID: 40004807
- PMCID: PMC11856960
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14041277
Advancements in Diagnostic Methods and Imaging Technologies in Dentistry: A Literature Review of Emerging Approaches
Abstract
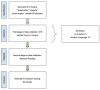
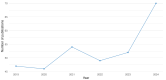
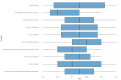
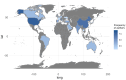
Introduction: Recent advancements in diagnostic imaging technologies have significantly improved the field of dental medicine. This review examines these new imaging techniques and their impact on enhancing accuracy, enabling early detection, and facilitating effective treatment planning in dentistry. Methods: A bibliometric and content analysis was conducted on 61 peer-reviewed articles retrieved from the Scopus database, published between 2019 and 2024. The selection criteria focused on studies exploring advances in dental diagnosis through innovative imaging methods and personalized techniques for identifying oral pathologies. The bibliometric approach analyzed publication trends, while content analysis categorized emerging technologies and their clinical applications. Results: Our findings indicate a notable shift towards integrating cutting-edge technologies, including Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT), artificial intelligence (AI), and biosensors. These advancements have significantly improved diagnostic accuracy, particularly in complex cases such as periodontal diseases, dental fractures, and oral infections. Studies demonstrate that molecular diagnostics and AI-driven algorithms enhance the personalization of treatment plans, optimizing patient outcomes. Conclusions: Emerging diagnostic technologies have the potential to enhance both the quality and efficiency of dental care. However, their implementation is challenged by high costs, the need for specialized training, and disparities in access. Future research should focus on refining AI-driven diagnostic models, addressing regulatory considerations, and expanding the clinical validation of novel imaging tools. As these technologies evolve, they are expected to increase diagnostic specificity, leading to more precise, patient-centered treatment approaches. Ultimately, these advancements offer substantial opportunities to transform dental practice by providing faster, less invasive, and more reliable diagnoses.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; biosensors; cone beam computed tomography; dentistry; diagnostic; imaging; technologies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Arjun A., Premkumar H.B., Jairam L.S., Sharma S.C., Nagabhushana H., Darshan G.P. Leveraging photosensitive and thermally stable luminescent Ba2ZnWO6:Eu3+, M+ (M+= Na, K, and Li) nanophosphor for targeted non-invasive and stain-free visualization of cracked tooth syndrome. Mater. Today Nano. 2024;28:100531. doi: 10.1016/j.mtnano.2024.100531. - DOI
-
- Gowdar I.M., Alateeq A.A., Alnawfal A.M.A., Alharbi A.F.A., Alhabshan A.M.S., Aldawsari S.M.S., Alharbi N.A.H. Artificial Intelligence and its Awareness and Utilization among Dental Studentsand Private Dental Practitioners at Alkharj, Saudi Arabia. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2024;16:S2264. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_188_24. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agwan M.A.S. Micro-Computed Tomography as a Transformative Tool in Endodontics: A Narrative Review. Med. Forum Mon. 2023;34:115.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

