Potential MRI Biomarkers for Predicting Kidney Function and Histological Damage in Transplanted Deceased Donor Kidney Recipients
- PMID: 40004881
- PMCID: PMC11856860
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14041349
Potential MRI Biomarkers for Predicting Kidney Function and Histological Damage in Transplanted Deceased Donor Kidney Recipients
Abstract
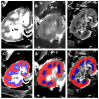
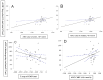
Background/Objectives: Kidney transplantation (kTx) is the preferred treatment for end-stage kidney disease. Limited evaluation of structural changes in transplanted kidneys hinders the timely prediction of disease progression and the implementation of treatment modifications. Protocol biopsies provide valuable insights but are invasive and carry risks of biopsy-related complications. This study investigates whether multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), including T1 and T2 mapping and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), can predict kidney function and the progression of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IF/TA) in the early post-transplant period. Methods: A prospective study was conducted at The Hospital of Lithuanian University of Health Sciences Kauno Klinikos from May 2022 to March 2024. Thirty-four patients receiving kidney transplants from deceased donors underwent baseline biopsies and post-transplant MRI scans. Follow-up assessments included kidney function evaluation, biopsies, and MRI scans at three months post-transplant. Results: Significant correlations were observed between MRI parameters and kidney function: T1 and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) corticomedullary differentiation (CMD) correlated with eGFR at discharge (r = -0.338, p = 0.05; r = 0.392, p = 0.022, respectively). Linear and logistic regression models demonstrated that post-transplant T1 and ADC CMD values significantly predicted kidney function at discharge. Furthermore, T1 CMD values measured 10-15 days post-transplant predicted IF/TA progression at three months post-kTx, with an area under the curve of 0.802 (95% CI: 0.616-0.987, p = 0.001) and an optimal cut-off value of -149.71 ms. The sensitivity and specificity were 0.818 and 0.273, respectively (Youden's index = 0.545). T2 mapping was not predictive. Conclusions: This study highlights the potential immediate clinical utility of MRI-derived biomarkers, particularly ADC and T1 CMD, in centers equipped with advanced imaging capabilities as tools for assessing kidney function in the early post-transplant period. With an AUROC of 0.802, T1 CMD demonstrates strong discriminatory power for predicting IF/TA progression early in the post-transplant period.
Keywords: IF/TA (interstitial fibrosis/tubular atrophy); MRI (magnetic resonance imaging); chronic allograft nephropathy; kidney transplantation; non-invasive biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Provenzano M., Rotundo S., Chiodini P., Gagliardi I., Michael A., Angotti E., Borrelli S., Serra R., Foti D., De Sarro G., et al. Contribution of Predictive and Prognostic Biomarkers to Clinical Research on Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:5846. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165846. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

