Integrative Roles of Functional Foods, Microbiotics, Nutrigenetics, and Nutrigenomics in Managing Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity
- PMID: 40004938
- PMCID: PMC11858703
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17040608
Integrative Roles of Functional Foods, Microbiotics, Nutrigenetics, and Nutrigenomics in Managing Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity
Abstract
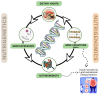
Diabetes and obesity are globally prevalent metabolic disorders posing significant public health challenges. The effective management of these conditions requires integrated and personalized strategies. This study conducted a systematic literature review, identifying 335 relevant papers, with 129 core articles selected after screening for duplicates and irrelevant studies. The focus of the study is on the synergistic roles of functional foods, microbiotics, and nutrigenomics. Functional foods, including phytochemicals (e.g., polyphenols and dietary fibers), zoochemicals (e.g., essential fatty acids), and bioactive compounds from macrofungi, exhibit significant potential in enhancing insulin sensitivity, regulating lipid metabolism, reducing inflammatory responses, and improving antioxidant capacity. Additionally, the critical role of gut microbiota in metabolic health is highlighted, as its interaction with functional foods facilitates the modulation of metabolic pathways. Nutrigenomics, encompassing nutrigenetics and genomics, reveals how genetic variations (e.g., single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)) influence dietary responses and gene expression, forming a feedback loop between dietary habits, genetic variations, gut microbiota, and metabolic health. This review integrates functional foods, gut microbiota, and genetic insights to propose comprehensive and sustainable personalized nutrition interventions, offering novel perspectives for preventing and managing type 2 diabetes and obesity. Future clinical studies are warranted to validate the long-term efficacy and safety of these strategies.
Keywords: diabetes; functional foods; microbiotics; nutrigenetics; nutrigenomics; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC) Worldwide trends in underweight and obesity from 1990 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 3663 population-representative studies with 222 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet. 2024;403:1027–1050. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)02750-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Siqueira J.S., Palacio T.L.N., Vieira T.A., Nakandakare-Maia E.T., Grandini N.A., Ferron A.J.T., Francisqueti-Ferron F.V., Correa C.R. An overview of the complex interaction between obesity and target organ dysfunction: Focus on redox-inflammatory state. Nutrire. 2023;48:21. doi: 10.1186/s41110-023-00206-x. - DOI
-
- Magliano D.J., Boyko E.J., IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th Edition Scientific Committee . IDF Diabetes Atlas. International Diabetes Federation; Brussels, Belgium: 2021.
-
- Romero-Cortes T., Lopez-Perez P., Toledo A., Perez-Espana V., Aparicio-Burgos J., Cuervo-Parra J. Nutrigenomics and nutrigenetics in functional foods. Int. J. Bio-Resour. Stress Manag. 2018;9:661–672. doi: 10.23910/IJBSM/2018.9.6.1922. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

