Polyphenol-Based Prevention and Treatment of Cancer Through Epigenetic and Combinatorial Mechanisms
- PMID: 40004944
- PMCID: PMC11858336
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17040616
Polyphenol-Based Prevention and Treatment of Cancer Through Epigenetic and Combinatorial Mechanisms
Abstract
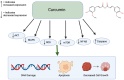
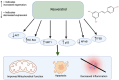
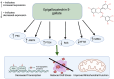
Polyphenols have been shown to be utilized as an effective treatment for cancer by acting as a DNMT or HDAC inhibitor, reducing inflammatory processes, and causing cell cycle arrest. While there have been many studies demonstrating the anti-cancerous potential of individual polyphenols, there are limited studies on the combinatorial effects of polyphenols. This review focuses on how combinations of different polyphenols can be used as a chemotherapeutic treatment option for patients. Specifically, we examine the combinatorial effects of three commonly used polyphenols: curcumin, resveratrol, and epigallocatechin gallate. These combinations have been shown to induce apoptosis, prevent colony formation and migration, increase tumor suppression, reduce cell viability and angiogenesis, and create several epigenetic modifications. In addition, these anti-cancerous effects were synergistic and additive. Thus, these findings suggest that using different combinations of polyphenols at the appropriate concentrations can be used as a better and more efficacious treatment against cancer as compared to using polyphenols individually.
Keywords: cancer; combination; dietary polyphenols; epigenetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zagoskina N.V., Zubova M.Y., Nechaeva T.L., Kazantseva V.V., Goncharuk E.A., Katanskaya V.M., Baranova E.N., Aksenova M.A. Polyphenols in Plants: Structure, Biosynthesis, Abiotic Stress Regulation, and Practical Applications (Review) Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023;24:13874. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813874. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

