Preparation of Highly Antibacterial Polyethersulfone/Sulfonated Polyethersulfone Blend Composite Membrane and Research on Its Dye Separation Performance
- PMID: 40005093
- PMCID: PMC11858200
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30040781
Preparation of Highly Antibacterial Polyethersulfone/Sulfonated Polyethersulfone Blend Composite Membrane and Research on Its Dye Separation Performance
Abstract
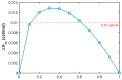
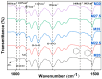
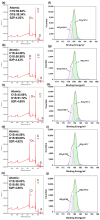
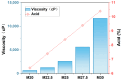
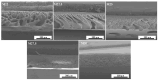
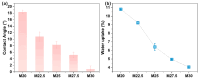
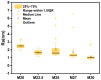
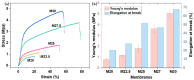
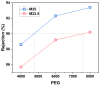
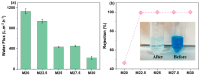
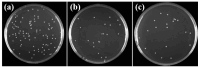
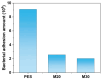
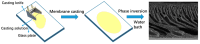
Bringing sulfonic acid groups into conventional polyethersulfone (PES) materials to prepare PES/sulfonated polyethersulfone (SPES) composite membranes has been shown to markedly enhance the hydrophilicity of the membranes and boost their separation efficiency in water treatment applications. However, membrane fouling due to microbial activity remains a critical challenge in the practical use of these membranes. Despite this, research into the antibacterial capabilities of PES/SPES composite membranes is scarce. This study employed the nonsolvent-induced phase inversion technique to prepare PES/SPES blend membranes and examined how the solid content influences their microstructure and separation performance. The findings indicated that an increase in solid content leads to higher casting solution viscosity, a reduction in membrane porosity from 10.8% to 4.06%, an increase in tensile strength from 0.79 MPa to 5.06 MPa, and a significant improvement in methylene blue rejection from 50% to nearly 100%. Additionally, the study revealed that the incorporation of SPES into the blend membranes enhances their resistance to bacterial adhesion, effectively suppressing microbial growth. Notably, the higher the sulfonic acid group content, the better the antibacterial properties of the composite membranes.
Keywords: PES; SPES; antibacterial properties; composite membrane; dye separation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nthunya L.N., Chong K.C., Lai S.O., Lau W.J., López-Maldonado E.A., Camacho L.M., Shirazi M.M.A., Ali A., Mamba B.B., Osial M., et al. Progress in membrane distillation processes for dye wastewater treatment: A review. Chemosphere. 2024;360:142347. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.142347. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Geise G.M., Lee H., Miller D.J., Freeman B.D., McGrath J.E., Paul D.R. Water purification by membranes: The role of polymer science. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2010;48:1685–1718. doi: 10.1002/polb.22037. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

