High Sensitivity and Selectivity of PEDOT/Carbon Sphere Composites for Pb2+ Detection
- PMID: 40005110
- PMCID: PMC11857889
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30040798
High Sensitivity and Selectivity of PEDOT/Carbon Sphere Composites for Pb2+ Detection
Abstract
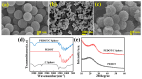
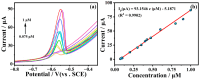
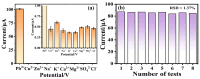
Heavy metal ions impair human health and irreversibly damage the ecosystem. As a result, it is critical to create an efficient approach for identifying heavy metal ions. The electrochemical sensor method is a type of detection method that is highly sensitive, low in cost, and allows for real-time monitoring. In this study, solid carbon spheres were made using resorcinol and formaldehyde as raw materials, followed by the formation of PEDOT/carbon sphere composites via in situ oxidative polymerization, and Pb2+ was detected utilizing them as electrode modification materials. The structure of the PEDOT/carbon spherical composites was analyzed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). To investigate the electrochemical properties of these composites, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), cyclic voltammetry (CV), and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) were employed. In addition, the detection mechanism of the material for Pb2⁺ was studied using CV. The PEDOT/carbon sphere sensor showcased an extensive linear detection range of 7.5 × 10-2 to 1.0 μM for Pb2+ ions, achieving a low limit of detection (LOD) of 3.5 × 10-2 nM and displaying exceptional selectivity. These results can be attributed to its large surface area, superior electrical conductivity, and outstanding electron transport properties. This study offers an effective material for detecting low concentrations of Pb2+, with potential applications in future Pb2+ detection.
Keywords: Pb2+ detection; Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene); carbon sphere; electrochemical sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors affirm that they have no acknowledged conflicting financial interests or personal affiliations that might have seemed to affect the work described in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A bromine-catalysis-synthesized poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/graphitic carbon nitride electrochemical sensor for heavy metal ion determination.RSC Adv. 2019 Oct 28;9(60):34691-34698. doi: 10.1039/c9ra02161b. eCollection 2019 Oct 28. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35530671 Free PMC article.
-
Facile one-pot method of AuNPs/PEDOT/CNT composites for simultaneous detection of dopamine with a high concentration of ascorbic acid and uric acid.RSC Adv. 2022 May 18;12(24):15038-15045. doi: 10.1039/d2ra01262f. eCollection 2022 May 17. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 35702427 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical Sensors based on Gold-Silver Core-Shell Nanoparticles Combined with a Graphene/PEDOT:PSS Composite Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode for Paraoxon-ethyl Detection.ACS Omega. 2024 Jan 2;9(2):2896-2910. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c08349. eCollection 2024 Jan 16. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38250352 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical Sensor of Double-Thiol Linked PProDOT@Si Composite for Simultaneous Detection of Cd(II), Pb(II), and Hg(II).Polymers (Basel). 2019 May 7;11(5):815. doi: 10.3390/polym11050815. Polymers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31067664 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical detection and quantification of catechol based on a simple and sensitive poly(riboflavin) modified carbon nanotube paste electrode.Heliyon. 2023 Mar 8;9(3):e14378. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14378. eCollection 2023 Mar. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36942251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Malik L.A., Bashir A., Qureashi A., Pandith A.H. Detection and removal of heavy metal ions: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019;17:1495–1521. doi: 10.1007/s10311-019-00891-z. - DOI
-
- Gao S., Xu C., Yalikun N., Mamat X., Li Y., Wågberg T., Hu X., Liu J., Luo J., Hu G. Sensitive and Selective Differential Pulse Voltammetry Detection of Cd(II) and Pb(II) Using Nitrogen-Doped Porous Carbon Nanofiber Film Electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017;164:H967. doi: 10.1149/2.1611713jes. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

