Algal Lectin Griffithsin Inhibits Ebola Virus Infection
- PMID: 40005201
- PMCID: PMC11858388
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30040892
Algal Lectin Griffithsin Inhibits Ebola Virus Infection
Abstract
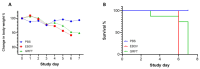
Algal lectin Griffithsin (GRFT) is a well-known mannose-binding protein which has broad-spectrum antiviral activity against several important infectious viruses including HIV, HCV, and SARS-CoV-2. Therefore, GRFT has been brought great attention to antiviral therapeutic development. In this report, we have tested GRFT's activity against the lethal Ebola virus in vitro and in vivo. Our data have shown that the IC50 value is about 42 nM for inhibiting Zaire Ebola virus (EBOV) infection in vitro. The preliminary in vivo mice model using mouse-adapted EBOV has also shown a certain efficacy for delayed mortality compared to the control animals. A GRFT pull-down experiment using viral particles demonstrates that GRFT can bind to N-glycans of EBOV. Thus, it can be concluded that GRFT, through binding to viral glycans, may block Ebola virus infection and has potential for the treatment of Ebola virus disease (EVD).
Keywords: Ebola virus (EBOV); Ebola virus disease (EVD); algal lectin; carbohydrate-binding; griffithsin (GRFT); mannose-binding.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Marc E. Mattix was employed by the company Nonclinical Pathology Services, LLC. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Mori T., O’Keefe B.R., Sowder R.C., 2nd, Bringans S., Gardella R., Berg S., Cochran P., Turpin J.A., Buckheit R.W., Jr., McMahon J.B., et al. Isolation and characterization of griffithsin, a novel HIV-inactivating protein, from the red alga Griffithsia sp. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:9345–9353. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411122200. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

