Characteristics and Mechanism of Ammonia Nitrogen Removal by Heterotrophic Nitrification Bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae LCU1 and Its Application in Wastewater Treatment
- PMID: 40005663
- PMCID: PMC11857964
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13020297
Characteristics and Mechanism of Ammonia Nitrogen Removal by Heterotrophic Nitrification Bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae LCU1 and Its Application in Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
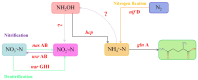
In this study, a novel strain exhibiting heterotrophic nitrification was screened; subsequently, the strain was identified as Klebsiella pneumoniae LCU1 using 16S rRNA gene sequencing. The aim of the study was to investigate the effects of external factors on the NH4+-N removal efficiency of strain LCU1 in order to elucidate the optimal conditions for NH4+-N removal by the strain and improve the removal efficiency. The findings indicated that the NH4+-N removal efficiency of the strain exceeded 80% under optimal conditions (sodium succinate carbon source, C/N ratio of 10, initial pH of 8.0, temperature of 30 °C, and speed of 180 rpm). The genome analysis of strain LCU1 showed that key genes involved in nitrogen metabolism, including narGHI, nirB, nxrAB, and nasAB, were successfully annotated; hao and amo were absent, but the nitrogen properties analysis determined that the strain had a heterotrophic nitrification ability. After 120 h, the NH4+-N removal efficiency of strain LCU1 was 34.5% at a high NH4+-N concentration of 2000 mg/L. More importantly, the NH4+-N removal efficiency of this strain was above 34.13% at higher Cu2+, Mn2+, and Zn2+ ion concentrations. Furthermore, strain LCU1 had the highest NH4+-N removal efficiency of 34.51% for unsterilised (LCU1-OC) aquaculture wastewater. This suggests that with intensive colonisation treatment, the strain has promising application potential in real wastewater treatment.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae; heterotrophic nitrification; wastewater treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Gu Y., Wei Y., Xiang Q., Zhao K., Yu X., Zhang X., Li C., Chen Q., Xiao H., Zhang X. C:N ratio shaped both taxonomic and functional structure of microbial communities in livestock and poultry breeding wastewater treatment reactor. Sci. Total Environ. 2019;651:625–633. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.234. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang Q., Kong J., Liang J., El-Din M.G., Zhao P., Xie W., Chen C. Nitrogen removal intensification of aerobic granular sludge through bioaugmentation with “heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification” consortium during petroleum wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2022;361:127719. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127719. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 2019JZZY010709/Provincial Major Scientific and Technological Innovation Projects in Shandong Province
- 319312105-20/the Open Project of Liaocheng Universtiy Animal Husbandry Discipline
- ZR2023QC241/the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- 31946220708/the LiaoCheng University Doctoral Research Initiation Fund (318052236), the Open Project of Liao Cheng University Animal Husbandry
- CXCY2023249,CXCY2023286,CXCY262, CXCY263/the Liao Cheng University Undergraduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

