Antibiotic Resistance Profiles and Genomic Analysis of Endophytic Bacteria Isolates from Wild Edible Fungi in Yunnan
- PMID: 40005728
- PMCID: PMC11858796
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13020361
Antibiotic Resistance Profiles and Genomic Analysis of Endophytic Bacteria Isolates from Wild Edible Fungi in Yunnan
Abstract
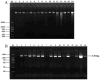
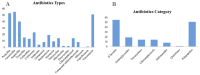
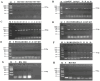
The use of antibiotics has led to the emergence of antibiotic resistance, posing significant challenges in the prevention, control, and treatment of microbial diseases, while threatening public health, the environment, and food safety. In this study, the antibiotic resistance phenotypes and genotypes of 56 endophytic bacteria isolates from three species of wild edible fungi in Yunnan were analyzed using the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method and PCR amplification. The results revealed that all isolates were sensitive to ofloxacin, but resistance was observed against 17 other antibiotics. Specifically, 55, 53, and 51 isolates exhibited resistance to amoxicillin, penicillin, and vancomycin, respectively. Antibiotic resistance gene (ARG) detection indicated that the sulfonamide sul1 gene had the highest detection rate (53.57%). Excluding the ARG that was not detected, the lowest detection rates were the sulfonamide sul2 and sul3 genes, both at 1.79%. Among six tetracycline resistance genes, only tetK and tetM were detected. For β-lactam antibiotics, blaTEM, blaVIM, and blaSHV genes were present, while blaOXA was absent. In aminoglycoside resistance genes, aadB was not detected, while detection rates for aac(3')-IIa, acrB, and aadA1 were 3.57%, 1.79%, and 37.5%, respectively. The chloramphenicol Cat gene was detected at a rate of 14.29%, whereas floR was absent. For polypeptide resistance, VanC was detected at 3.57%, with EmgrB not detected. All three quinolone genes were detected, with detection rates of 8.92% for GyrA, 39.29% for GyrB, and 37.5% for ParC. Through phylogenetic analysis, 12 isolates that are closely related to ten common foodborne pathogenic bacteria were further selected for whole-genome sequencing and assembly. Gene annotations revealed that each isolate contained more than 15 ARGs and over 30 virulence factors. Notably, the detection rate of antibiotic resistance phenotypes was higher than that of genotypes, highlighting the importance of studying phenotypic antibiotic resistance that lacks identifiable ARGs. This study enriches the research on endophytes in wild edible fungi and provides new data for microbial ecology and antibiotic resistance research. It also offers critical insights for monitoring microbial antibiotic resistance in wild edible fungi and potentially other food sources, contributing to more effective strategies for ecological protection, sustainable agricultural development, and public health security.
Keywords: ARG; antibiotics resistance; endophytic bacteria; foodborne pathogens; genome assembly; wild edible fungi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Huang X.Z., Zhao F.L. Mechanism of endophytes of medicinal plants in promoting the growth of host plants. Microbiol. China. 2023;50:1653–1665. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.221120. - DOI
-
- Vandana U.K., Rajkumari J., Singha L.P., Satish L., Alavilli H., Sudheer P.D., Chauhan S., Ratnala R., Satturu V., Mazumder P.B. The endophytic microbiome as a hotspot of synergistic interactions, with prospects of plant growth promotion. Biology. 2021;10:101. doi: 10.3390/biology10020101. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu M.J., Xu Y.J., Huang X.Z., Zhao F.L. Advances in research methods for plant endophytes. Microbiol. China. 2024;51:1887–1897. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.230976. - DOI
-
- Tang M.-J., Lu F., Yang Y., Sun K., Zhu Q., Xu F.-J., Zhang W., Dai C.-C. Benefits of endophytic fungus Phomopsis liquidambaris inoculation for improving mineral nutrition, quality, and yield of rice grains under low nitrogen and phosphorus condition. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2022;41:2499–2513. doi: 10.1007/s00344-021-10462-8. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

