Paeoniflorin Inhibits Porcine Circovirus Type 2 Replication by Inhibiting Autophagy and Targeting AKT/mTOR Signaling
- PMID: 40005877
- PMCID: PMC11860941
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci12020117
Paeoniflorin Inhibits Porcine Circovirus Type 2 Replication by Inhibiting Autophagy and Targeting AKT/mTOR Signaling
Abstract
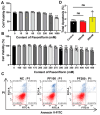
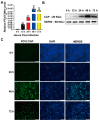
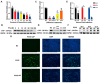
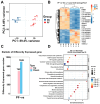
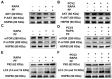
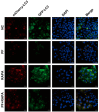
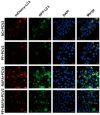
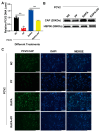
Porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) is an important pathogen that leads to great economic losses to the swine industry. Paeoniflorin (PF), a novel plant extract, has been reported to have antiviral properties. However, the role of paeoniflorin in regulating PCV2 replication remains unclear. Here, we used the CCK8 assay to demonstrate that PF within safe concentrations (0-275 mM) significantly inhibits PCV2 replication in a dose-dependent manner in porcine kidney cells. Subsequently, comparative transcriptome and functional verification revealed that PF probably inherits PCV2 replication via targeting AKT/mTOR signaling. Further experimental data show that the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway is highly relevant to autophagy. Thus, experimental data from Western blot, qPCR, and the indirect immunofluorescence test indicate that PF inhibits PCV2 replication by inhibiting autophagy by targeting the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Together, our results provide insight into the mechanism of paeoniflorin in regulating PCV2 replication and offer new ideas for the treatment of PCV2 infection in pigs.
Keywords: AKT/mTOR signaling; autophagy; paeoniflorin; porcine circovirus type 2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

