HDAC/σ1R Dual-Ligand as a Targeted Melanoma Therapeutic
- PMID: 40005993
- PMCID: PMC11859726
- DOI: 10.3390/ph18020179
HDAC/σ1R Dual-Ligand as a Targeted Melanoma Therapeutic
Abstract
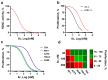
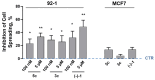
Background: In melanoma, multiligand drug strategies to disrupt cancer-associated epigenetic alterations and angiogenesis are particularly promising. Here, a novel dual-ligand with a single shared pharmacophore capable of simultaneously targeting histone deacetylases (HDACs) and sigma receptors (σRs) was synthesized and subjected to phenotypic in vitro screening. Methods: Tumor cell proliferation and spreading were investigated using immortalized human cancer and normal cell lines. Angiogenesis was also evaluated in mouse endothelial cells using a tube formation assay. Results: The dual-ligand compound exhibited superior potency in suppressing both uveal and cutaneous melanoma cell viability compared to other cancer cell types or normal cells. Melanoma selectivity reflected inhibition of the HDAC-dependent epigenetic regulation of tumor proliferative kinetics, without involvement of σR signaling. In contrast, the bifunctional compound inhibited the formation of capillary-like structures, formed by endothelial cells, and tumor cell spreading through the specific regulation of σ1R signaling, but not HDAC activity. Conclusions: Together, the present findings suggest that dual-targeted HDAC/σ1R ligands might efficiently and simultaneously disrupt tumor growth, dissemination and angiogenesis in melanoma, a strategy amenable to future clinical applications in precision cancer treatment.
Keywords: HDACi; angiogenesis; cancer proliferation; cell spreading; dual-ligands; melanoma; σ1 receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
C.G.L. is an employee at Vera Salus Ricerca S.r.l. G.M.P. is a shareholder and the Chief Science Officer at Vera Salus Ricerca S.r.l. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest. The company had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





References
-
- Clark W.H.J., From L., Bernardino E.A., Mihm M.C. The histogenesis and biologic behavior of primary human malignant melanomas of the skin. Cancer Res. 1969;29:705–727. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

