Andrographolide Sulfonates and Xiyanping: A Review of Chemical Composition, Pharmacological Activities, Clinical Applications, and Adverse Reactions
- PMID: 40005997
- PMCID: PMC11859262
- DOI: 10.3390/ph18020183
Andrographolide Sulfonates and Xiyanping: A Review of Chemical Composition, Pharmacological Activities, Clinical Applications, and Adverse Reactions
Abstract
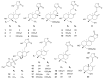
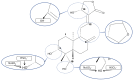
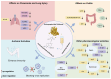
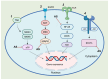
Andrographis paniculata is a plant of the Acanthaceae family and its primary bioactive constituent, andrographolide, exhibits a broad spectrum of pharmacological activities and notable clinical efficacy. However, its poor solubility and limited bioavailability pose significant challenges for therapeutic applications. To overcome these limitations, researchers have synthesized andrographolide sulfonates by reacting andrographolide with ethanol and sulfuric acid. This sulfonated derivative significantly enhances water solubility and bioavailability while retaining key pharmacological properties such as anti-inflammatory and antiviral activities. As a representative formulation, Xiyanping injection has been widely employed in the treatment of respiratory infections, pneumonia, and related conditions, playing a critical role during the COVID-19 pandemic. Despite its widespread application, there has yet to be a comprehensive review of its chemical composition and pharmacological mechanisms. Additionally, the safety of Xiyanping injection remains a topic of some debate. This review systematically examines the chemical composition, pharmacological activities, clinical applications, and adverse reactions of andrographolide sulfonates and their formulation in Xiyanping injection to provide a scientific basis for further research and applications, while also offering valuable insights for the development of similar sulfonated drugs.
Keywords: adverse reaction; andrographolide sulfonate; anti-inflammatory; antiviral activities; chemical composition; clinical application; pharmacological activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology of Andrographis paniculata and Its Major Bioactive Phytoconstituent Andrographolide.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:846740. doi: 10.1155/2013/846740. Epub 2013 Mar 24. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23634174 Free PMC article.
-
Current Trends on Repurposing and Pharmacological Enhancement of Andrographolide.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(12):2346-2368. doi: 10.2174/0929867327666200810135604. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32778020 Review.
-
Overview of pharmacological activities of Andrographis paniculata and its major compound andrographolide.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(sup1):S17-S29. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1501657. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30040451
-
Adverse Effects of Andrographolide Derivative Medications Compared to the Safe use of Herbal Preparations of Andrographis paniculata: Results of a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Studies.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 28;13:773282. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.773282. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35153776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An insight into the pharmacological and analytical potential of Andrographolide.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2022 Aug;36(4):586-600. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12757. Epub 2022 Jan 23. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35001431 Review.
References
-
- Hossain S., Urbi Z., Karuniawati H., Mohiuddin R.B., Moh Qrimida A., Allzrag A.M.M., Ming L.C., Pagano E., Capasso R. Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Wall. Ex Nees: An Updated Review of Phytochemistry, Antimicrobial Pharmacology, and Clinical Safety and Efficacy. Life. 2021;11:348. doi: 10.3390/life11040348. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission . Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Volume 1. China Medical Science Press; Beijing, China: 2020. p. 329.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

