Exploring the Potential of Gold Nanoparticles in Proton Therapy: Mechanisms, Advances, and Clinical Horizons
- PMID: 40006543
- PMCID: PMC11859620
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17020176
Exploring the Potential of Gold Nanoparticles in Proton Therapy: Mechanisms, Advances, and Clinical Horizons
Abstract
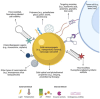
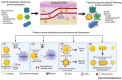
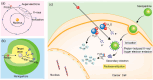
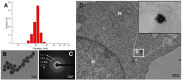
Proton therapy represents a groundbreaking advancement in cancer radiotherapy, leveraging the unique spatial energy distribution of protons to deliver precise, high-dose radiation to tumors while sparing surrounding healthy tissues. Despite its clinical success, proton therapy faces challenges in optimizing its therapeutic precision and efficacy. Recent research has highlighted the potential of gold nanoparticles to enhance proton therapy outcomes. Due to their high atomic number and favorable biological properties, gold nanoparticles act as radiosensitizers by amplifying the generation of secondary electrons and reactive oxygen species upon proton irradiation. This enhances DNA damage in tumor cells while preserving healthy tissues. Additionally, functionalization of gold nanoparticles with tumor-targeting ligands offers improved precision, making proton therapy more effective against a broader range of cancers. This review synthesizes current knowledge on the mechanisms of gold nanoparticle radiosensitization, preclinical evidence, and the technological hurdles that must be addressed to integrate this promising approach into clinical practice, aiming to advance the efficacy and accessibility of proton therapy in cancer therapy.
Keywords: cancer therapy; gold nanoparticles; precision medicine; proton therapy; radiosensitization; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Gold nanoparticle enhanced proton therapy: A Monte Carlo simulation of the effects of proton energy, nanoparticle size, coating material, and coating thickness on dose and radiolysis yield.Med Phys. 2020 Feb;47(2):651-661. doi: 10.1002/mp.13923. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 31725910
-
Radiosensitization Effect of Gold Nanoparticles in Proton Therapy.Front Public Health. 2021 Jul 29;9:699822. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.699822. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34395371 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Proton Therapy Efficacy Through Nanoparticle-Mediated Radiosensitization.Cells. 2024 Nov 7;13(22):1841. doi: 10.3390/cells13221841. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39594590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modelling direct DNA damage for gold nanoparticle enhanced proton therapy.Nanoscale. 2017 Nov 30;9(46):18413-18422. doi: 10.1039/c7nr07310k. Nanoscale. 2017. PMID: 29148554
-
Gold Nanoparticles as Radiosensitizers in Cancer Radiotherapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Nov 24;15:9407-9430. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S272902. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33262595 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gold Nanoparticle-Enhanced Production of Reactive Oxygen Species for Radiotherapy and Phototherapy.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Feb 19;15(4):317. doi: 10.3390/nano15040317. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39997879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Cancer Cell Fate: Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Gold Nanoparticles in Treatment Strategies.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jun 14;47(6):460. doi: 10.3390/cimb47060460. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699859 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chong L.M., Tng D.J.H., Tan L.L.Y., Chua M.L.K., Zhang Y. Recent advances in radiation therapy and photodynamic therapy. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2021;8:041322. doi: 10.1063/5.0060424. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

