LB-100 Enhances Drugs Efficacy Through Inhibition of P-Glycoprotein Expression in Multidrug-Resistant Glioblastoma and Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Cellular Models
- PMID: 40006556
- PMCID: PMC11859366
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17020189
LB-100 Enhances Drugs Efficacy Through Inhibition of P-Glycoprotein Expression in Multidrug-Resistant Glioblastoma and Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Cellular Models
Abstract
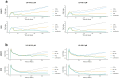
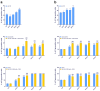
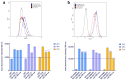
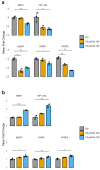
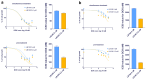
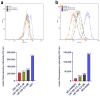
Background/Objectives: This study explores the potential of LB-100 (a protein phosphatase 2A-PP2A inhibitor) combined with adavosertib (a WEE1 kinase inhibitor) and doxorubicin (DOX), to overcome multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer cells and enhance treatment efficacy. Methods: We evaluated LB-100 combinations with adavosertib and DOX in patient-derived glioblastoma and non-small cell lung carcinoma cells (NSCLCs) using a real-time cell analyzer. Effectiveness was also assessed through immunofluorescence assay, and interactions were analyzed via SynergyFinder+. We also examined P-glycoprotein (P-gp) expression and drug resistance genes' expression in MDR glioblastoma and NSCLCs after LB-100 treatment, as well as LB-100 sensitizing effect on DOX and DOX accumulation. Results: LB-100 significantly boosts the effectiveness of adavosertib and DOX after multiple applications. It also enhances these drugs' cytotoxicity in a single application without acting synergistically. Additionally, LB-100 reduces P-gp expression in MDR glioblastoma and NSCLCs, sensitizing them to DOX and increasing its accumulation. Conclusions: LB-100 enhances the effectiveness of drugs against MDR cancer cells, presenting a promising strategy to overcome drug resistance in glioblastoma and NSCLCs through P-gp modulation.
Keywords: LB-100; P-glycoprotein; adavosertib; doxorubicin; glioblastoma; multidrug resistance; non-small cell lung carcinoma; protein phosphatase 2A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reversing Multidrug Resistance in Chemo-resistant Human Lung Adenocarcinoma (A549/DOX) Cells by Algerian Propolis Through Direct Inhibiting the P-gp Efflux-pump, G0/G1 Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis Induction.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018;18(9):1330-1337. doi: 10.2174/1871520618666180808100800. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30088453
-
Hypoxia can impair doxorubicin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting MRP1 and P-gp expression and boosting the chemosensitizing effects of MRP1 and P-gp blockers.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2016 Oct;39(5):411-433. doi: 10.1007/s13402-016-0285-5. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2016. PMID: 27306525
-
Effects of amiodarone, cyclosporin A, and PSC 833 on the cytotoxicity of mitoxantrone, doxorubicin, and vincristine in non-P-glycoprotein human small cell lung cancer cell lines.Cancer Res. 1994 Oct 15;54(20):5368-73. Cancer Res. 1994. PMID: 7923167
-
The use of liposomal anticancer agents to determine the roles of drug pharmacodistribution and P-glycoprotein (PGP) blockade in overcoming multidrug resistance (MDR).Anticancer Res. 1999 Jul-Aug;19(4B):2885-91. Anticancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10652569 Review.
-
Modulation of P-glycoprotein function and reversal of multidrug resistance by (-)-epigallocatechin gallate in human cancer cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2005 Apr;59(3):64-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2005.01.002. Biomed Pharmacother. 2005. PMID: 15795098 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

