Assessment of Cell Viability in Drug Therapy: IC50 and Other New Time-Independent Indices for Evaluating Chemotherapy Efficacy
- PMID: 40006615
- PMCID: PMC11859577
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17020247
Assessment of Cell Viability in Drug Therapy: IC50 and Other New Time-Independent Indices for Evaluating Chemotherapy Efficacy
Abstract
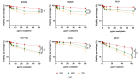
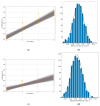
Background/Objectives: Cell viability assays play a crucial role in cancer research and the development of effective treatments. Evaluating the efficacy of conventional treatments across different tumor profiles is essential for understanding patient resistance to chemotherapy and relapse. The IC50 index has been commonly used as a guide in these assays. The idea behind the IC50 index is to compare cell proliferation under treatment with respect to a control population exposed to the same treatment. The index requires normalization to a control and is time dependent. These aspects are disadvantages, as small variations yield different results. In this article, we propose a new method to analyze cell viability assays. Methods: This method involves calculating the effective growth rate for both control (untreated) cells and cells exposed to a range of drug doses for short times, during which exponential proliferation can be assumed. The concentration dependence of the effective growth rate gives a real estimate of the treatment on cell proliferation. A curve fit of the effective growth rate related to concentration yields the concentration corresponding to a given effective growth rate. Results: We use this estimation to calculate the IC50 index and introduce two new parameters (ICr0 and ICrmed) to compare treatment efficacy under different culture conditions or cell lines. Conclusions: In summary, this study presents a new method to analyze cell viability assays and introduces two more precise parameters, improving the comparison and evaluation of efficacy under different conditions.
Keywords: IC50; cell viability; drug resistance; effective growth rate; mathematical model.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Clara E. Gavira-O’Neill and Raquel González-Martos are employed by the company Nageru S.L. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- World Health Organization. [(accessed on 10 August 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer.
-
- Altobelli E., Latella G., Morroni M., Licini C., Tossetta G., Mazzucchelli R., Profeta V.F., Coletti G., Leocata P., Castellucci M., et al. Low HtrA1 Expression in Patients with Long-Standing Ulcerative Colitis and Colorectal Cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2017;38:418–426. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5700. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Campagna R., Pozzi V., Giorgini S., Morichetti D., Goteri G., Sartini D., Serritelli E.N., Emanuelli M. Paraoxonase-2 Is Upregulated in Triple Negative Breast Cancer and Contributes to Tumor Progression and Chemoresistance. Hum. Cell. 2023;36:1108–1119. doi: 10.1007/s13577-023-00892-9. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

