Immunosuppressive Therapy Modifies Anti-Spike IgG Subclasses Distribution After Four Doses of mRNA Vaccination in a Cohort of Kidney Transplant Recipients
- PMID: 40006670
- PMCID: PMC11860609
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines13020123
Immunosuppressive Therapy Modifies Anti-Spike IgG Subclasses Distribution After Four Doses of mRNA Vaccination in a Cohort of Kidney Transplant Recipients
Abstract
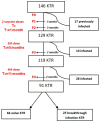
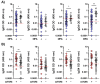
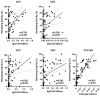
Background: IgG4 is the least immunogenic subclass of IgG. Immunization with mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2, unlike other vaccines, induces an increase in IgG4 against the spike protein in healthy populations. This study investigated whether immunosuppressive therapy affects the immune response, focusing on IgG subclass changes, to four doses of mRNA vaccine in kidney transplant recipients (KTRs). Methods: This study includes 146 KTRs and 23 dialysis patients (DPs) who received three mRNA-1273 vaccine doses and a BNT162b2 booster. We evaluated anti-spike IgG titers and subclasses, T-CD4+ and T-CD8+ cellular responses, and serum neutralizing activity (SNA). Results: At the fourth dose, 75.8% of COVID-19 naïve KTRs developed humoral and cellular responses (vs. 95.7% in DPs). There was a correlation between anti-spike IgG titers/subclasses and SNA (p < 0.001). IgG subclass kinetics after the third/fourth dose differed between COVID-19 naïve KTRs and DPs. Immunosuppressive therapy influenced IgG subclasses: mTOR inhibitors (mTORi) positively influenced IgG1 and IgG3 (p < 0.05), while mycophenolic acid negatively affected IgG1, IgG3, and IgG4 (p < 0.05). SNA is correlated with breakthrough infections after four doses of vaccine in KTRs. mTORi was the only factor associated with SNA > 65% in naïve KTRs [4.29 (1.21-15.17), p = 0.024]. Conclusions: KTRs show weaker cellular and humoral immune responses to mRNA vaccines and a class shift towards non-inflammatory anti-S IgG4 upon booster doses. IgG subclasses show a positive correlation with SNA and are influenced by immunosuppression. Increased SNA after four doses of vaccine is protective against infection. mTORi may benefit non-responding KTRs.
Keywords: COVID-19; IgG subclasses; SARS-CoV-2 vaccine; kidney transplant recipients; serum neutralizing activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A third COVID-19 vaccine dose in kidney transplant recipients induces antibody response to vaccine and Omicron variants but shows limited Ig subclass switching.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Mar 4;13(3):e0219024. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02190-24. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 39887251 Free PMC article.
-
Humoral and cellular immune response to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine in pediatric kidney transplant recipients compared with dialysis patients and healthy children.Pediatr Nephrol. 2023 Jul;38(7):2199-2208. doi: 10.1007/s00467-022-05813-w. Epub 2022 Dec 2. Pediatr Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36459243 Free PMC article.
-
A Third COVID-19 Vaccine Dose in Kidney Transplant Recipients Induces Antibody Response to Vaccine and Omicron Variants but Shows Limited Ig Subclass Switching.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 3:2024.09.01.610689. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.01.610689. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Mar 04;13(3):e0219024. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02190-24. PMID: 39282433 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Long-Term Humoral Response After a Second Dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine in Japanese Kidney Transplant Recipients.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jun 9;13:922042. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.922042. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35756063 Free PMC article.
-
Immunity against Delta and Omicron variants elicited by homologous inactivated vaccine booster in kidney transplant recipients.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 9;13:1042784. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1042784. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36700230 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wratil P.R., Stern M., Priller A., Willmann A., Almanzar G., Vogel E., Feuerherd M., Cheng C.-C., Yazici S., Christa C., et al. Three exposures to the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 by either infection or vaccination elicit superior neutralizing immunity to all variants of concern. Nat. Med. 2022;28:496–503. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01715-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pérez-Flores I., Juarez I., Meneses A.S.A., Lopez-Gomez A., Romero N.C., Rodriguez-Cubillo B., de la Higuera M.A.M., Peix-Jiménez B., Gonzalez-Garcia R., Baos-Muñoz E., et al. Role of mTOR inhibitor in the cellular and humoral immune response to a booster dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 vaccine in kidney transplant recipients. Front. Immunol. 2023;14:1111569. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1111569. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

