Evaluating the role of inflammatory biomarkers as a diagnostic tool in peri-implantitis
- PMID: 40008071
- PMCID: PMC11849608
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2025.01.015
Evaluating the role of inflammatory biomarkers as a diagnostic tool in peri-implantitis
Abstract
Background: Most studies have analyzed the presence of cytokines in Gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) in different periodontal diseases, but very limited studies have been conducted on Peri-implant crevicular fluid (PICF) in peri-implantitis.
Aim: The present study was conceptualized to explore the levels of Interleukin (IL)-1β and Interleukin (IL)-6 as a diagnostic marker in peri-implantitis.
Materials and methods: A total of 40 patients each having at least one dental implant were enrolled in the study. Clinical parameters were recorded around each implant and tooth nearest to it. Gingival crevicular fluid (GCF)/Peri-implant crevicular fluid (PICF) was collected to evaluate the concentration of IL-1β and IL-6. Conservative treatment was performed in peri-implantitis cases, 3 months after treatment their clinical parameters, IL-1β and IL-6 levels were recorded and compared with their pre-treatment values.
Results: Clinical parameters like Modified Plaque Index (MPI), Modified Bleeding Index (MBI) and Probing Pocket Depth (PPD) were statistically significantly higher in the peri-implantitis group as compared to the healthy implant group and healthy teeth group. IL-1β and IL-6 levels were also statistically significantly higher in the peri-implantitis group in comparison to healthy implants and healthy teeth group.
Conclusion: The study concludes that biomarkers in PICF can be used as a diagnostic tool to supplement the diagnosis of peri-implantitis along with the use of clinical parameters to make an early diagnosis of peri-implantitis possible.
Keywords: Healthy implant; Interleukin-1β; Interleukin-6; Peri-implantitis.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
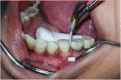
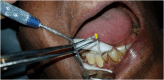
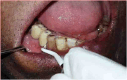
Nil (see Fig. 1, Fig. 2, Fig. 3, Fig. 4, Fig. 5, Fig. 6)Fig. 1IOPA of healthy implant case.Fig. 1Fig. 2Pooled PICF collection from healthy implant site.Fig. 2Fig. 3IOPA of implant suffering from peri-implantitis.Fig. 3Fig. 4Pooled PICF collection from peri-implantitis site.Fig. 4Fig. 5Pooled GCF collection from healthy teeth nearest to peri-implantitis site.Fig. 5Fig. 6Performing conservative therapy in peri-implantitis case.Fig. 6
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evaluation of gingival crevicular fluid and peri-implant crevicular fluid levels of sclerostin, TWEAK, RANKL and OPG.Cytokine. 2019 Jan;113:433-439. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.10.021. Epub 2018 Oct 28. Cytokine. 2019. PMID: 30377055
-
Comparison of interleukin-1β levels in gingival crevicular fluid and peri-implant crevicular fluid and its relationship with clinical indexes.J Dent (Tehran). 2013 Jan;10(1):1-9. Epub 2013 Jan 31. J Dent (Tehran). 2013. PMID: 23724197 Free PMC article.
-
Peri-implant crevicular fluid SIRT1 levels decrease in patients with peri-implant inflammatory: A prospective observational study.Transpl Immunol. 2022 Oct;74:101659. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2022.101659. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Transpl Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35781023
-
Peri-Implantitis Diagnosis and Prognosis Using Biomarkers in Peri-Implant Crevicular Fluid: A Narrative Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2019 Dec 7;9(4):214. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics9040214. Diagnostics (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31817894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines and osteoclastogenesis-related factors in peri-implant diseases: systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Jun 24;23(1):420. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03072-1. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37355561 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Role of artificial intelligence in transforming prosthodontics and oral implantology: in vivo study.Bioinformation. 2025 May 31;21(5):1275-1278. doi: 10.6026/973206300211275. eCollection 2025. Bioinformation. 2025. PMID: 40822779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simonis P, Dufour T, Tenenbaum H. Long-term implant survival and success. Clin Oral Implants Res2010; 21:772–777. - PubMed
-
- Khammissa R.A.G., Feller L., Meyerov R., Lemmer J. Peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: clinical and histopathological characteristics and treatment. SADJ. 2012;67:124–126. - PubMed
-
- Song Z., Weigl P., Wang B. Correlations of inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress markers, and matrix metalloproteinases in gingival crevicular fluid with peri-implantitis. Eur J Inflamm. 2019;17
-
- Mombelli A., Lang N.P. The diagnosis and treatment of peri-implantitis. Periodontol. 2000 1998;17:63–76. - PubMed
-
- Silness J., Loe H. Periodontal disease in pregnancy II Correlation between oral hygiene and periodontal condition. Acta Odontol Scand. 1964;22:121–135. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

